Bayan I (reigned 562/565-602 CE) was a king of the Avars, a confederation of heterogeneous people who migrated from the region of Mongolia, north of China, in 552 CE and came in contact with the Eastern Roman Empire c. 557 CE. Bayan I is considered the greatest king of the Avars for his military and political skills. He not only protected his people from the Gokturks, who pursued them from Mongolia after the fall of the Rouran Empire (known as the Rouran Khaganate) in the east, but he led them in a series of successful campaigns to defeat the Gepids of Pannonia, outwitted the Lombard king, Alboin, for control of the land, and challenged the supremacy of the Eastern Roman Empire. He founded the Avar Empire in the region of Pannonia, establishing his capital at the same spot that Attila the Hun had claimed as his own, and expanded that empire to encompass territory far beyond the original borders of the Pannonia they had first arrived in. After Bayan I's death in 602 CE, the Avar Empire began to decline until it was finally conquered by the Franks in 796 CE, and the Avars ceased to exist as a distinct cultural and political entity.
Bayan I & the Eastern Empire
Bayan I first enters history with the migration of the Avars to the region of the Pontic Grass Steppe (an area corresponding to modern-day Ukraine, Russia, Kazakhstan) from Central Asia after the fall of the Rouran Empire. They were pursued by their enemies the Gokturks, who had toppled the supremacy of the Rourans in Mongolia and, as refugees, they were seeking a secure homeland they could settle and then defend. The historian Erik Hildinger describes Bayan's initial rise to power following the Avar's migration: "Shortly thereafter, in 565, Bayan ascended the Avar throne as Kaghan, or Great Khan. The Avars were the first to use this term, which would persist thereafter among the steppe peoples. Bayan was the greatest of their leaders" (76).
The historian H.H. Howorth states how "The Avars were at this time led by a chief whom, if we knew more of, we should probably compare with Attila and Genghis Khan. His name was Bayan" (732). Bayan I is the first recorded king of the Avars and, like Attila, was the leader who unified and empowered his people. He raised the Avars from a band of refugees fleeing their oppressor to the dominant people of the region of Pannonia.
Regarding the origin of the Avars and their flight to the west, historian Peter Heather writes:
[The Avars] were the next major wave of originally nomadic horse warriors, after the Huns, to sweep off the Great Eurasian Steppe and build an empire in central Europe. Thankfully, we know rather more about them than about the Huns. The Avars spoke a Turkic language and had previously starred as the dominant force behind a major nomadic confederation on the fringes of China. In the earlier sixth century they had lost this position to a rival force, the so-called Western Turks [Gokturks], and arrived on the outskirts of Europe as political refugees, announcing themselves with an embassy that appeared at Justinian's court in 558. (401)
Although, as Heather claims, "we know more about [the Avars] than about the Huns", we know considerably less about Bayan I than Attila. After leading his people to the west, he almost immediately made contact with the emperor of the Byzantine Empire. Justinian I (482-565 CE) agreed to hire them to fight against other tribes in the region as mercenaries and sent them on their way. The Avars ruthlessly massacred the enemies of Justinian I and expected that their relationship with the empire would continue but, should it not, tried to find a region they could settle in.
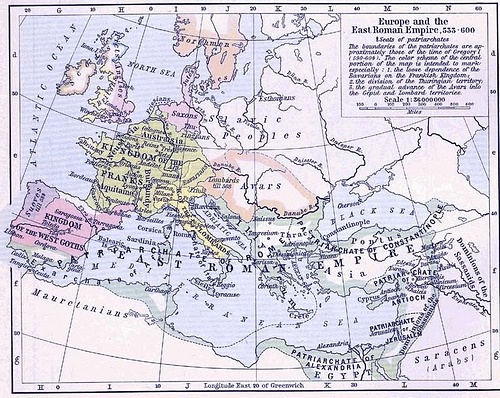
Although they were now employed by the powerful Byzantine Empire, they still needed their own homeland where they could feel secure from the pursuing Turks. Bayan I tried to lead his people south of the Danube River but was prevented by the Romans. He then led the Avars north but encountered resistance from the Franks under their king Sigebert I. They continued as nomads in the service of Rome until the death of Justinian in 565 CE. His successor, Justin II (c. 520-578 CE), canceled their contract and, when the Avar embassy asked for permission to cross the southern Danube, it was denied. They again sought to break through to the north but were repelled by Sigebert's army. Bayan I then turned his attention to Pannonia or, according to other sources, was invited to go there by Justin II to displace the Gepids.
Bayan I & Alboin
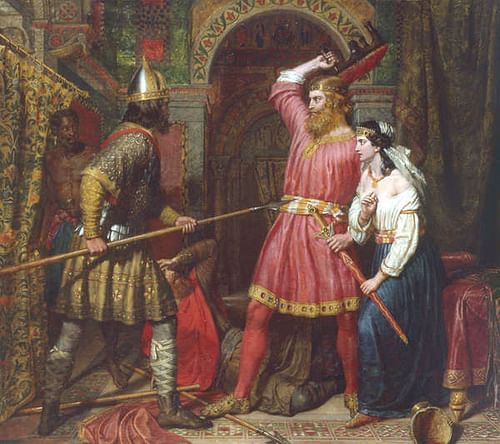
The Lombards under Alboin were already in Pannonia in conflict with the Gepids who controlled most of the region. As with the Avars, sources conflict on whether the Lombards migrated to Pannonia on their own or were invited by the empire to drive out the Gepids. Bayan I wanted to take the capital city of Sirmium but did not know the region and needed the help of those better acquainted with it. He allied himself with Alboin and the Lombards and, in 567 CE, the two armies joined to crush the Gepids between them. Bayan I had already negotiated the terms of the alliance with Alboin: if they should win, the Avars would be given the Gepid lands, wealth, and people as slaves and the Lombards could continue to live unmolested in the region. Alboin most likely agreed to these unequal terms because Bayan I threatened him with conquest if he refused. This remains speculation, however, and it is not known why Alboin chose to accept the poor terms of the alliance.

The armies met in battle some distance from Sirmium, and the Gepids, under their king Cunimund, were defeated. Sources differ on what happened in the aftermath: according to some accounts, Bayan I killed Cunimund and had his skull turned into a wine cup - which he then presented to Alboin as a comrade in arms while, according to others, Alboin killed Cunimund and made his skull into a cup which he then wore on his belt. Whomever it was that killed the Gepid king, his skull would later contribute to Alboin's death.
The armies of the Avars and Lombards marched on Sirmium, but the Gepids had already called for help from the Eastern Empire, agreeing to surrender the city to them in exchange for assistance; by the time Bayan I and Alboin reached Sirmium, it was heavily defended and they were driven back. Since they had not prepared themselves for an extended siege, the armies withdrew.
The Rise of the Avar Empire
Although Sirmium remained untaken, the Avars now controlled most of Pannonia and the Lombards found that the deal they had brokered earlier was a poor one. Alboin tried to form an alliance with the Gepids against the Avars by marrying Cunimund's daughter Rosamund whom he had taken after the battle. It was now too late, though, as the Avars were simply too powerful to contest. In 568 CE, Alboin led his people out of Pannonia to Italy where, in 572 CE, he would be assassinated in a plot hatched by his wife to avenge her father. According to Paul the Deacon, Alboin's murder was the result of his drunken insistence that his wife drink from her father's skull.
With the Lombards gone, and the Gepids defeated, Bayan I then set about building his empire on the plains of Pannonia. That there seems to have been a core "Avar" ethnicity among the larger Avar confederation is seen in some of Bayan I's military decisions and decrees. The historian and scholar Denis Sinor writes:
The ethnic composition of the Avar state was not homogeneous. Bayan was followed by 10,000 Kutrighur warrior subjects already at the time of the conquest of the Gepids. In 568 he sent them to invade Dalmatia, arguing that casualties they may suffer while fighting against the Byzantines would not hurt the Avars themselves. (222)
Under Bayan I's leadership, the Avars expanded across Pannonia in every direction and, through conquest, he enlarged his empire. A number of Slavic people had followed the Avars into Pannonia and these were now subjects of Avar rule and seemed to be treated with the same lack of regard accorded the Kutrighur soldiers. Bayan I oversaw the selection of the Avar base of operations in their new homeland. Historian Erik Hildinger comments on this, writing:
The Avars established their headquarters near Attila's old capital of a hundred years before and fortified it. It was known as The Ring. Now well established in Pannonia, Bayan fought the Franks of Sigebert again and defeated them in 570. A dozen years later Bayan attacked Byzantine territory and seized the city of Sirmium on the Sava River. He followed this with further campaigns against the Byzantines, the Avars taking Singidunum (Belgrade) and ravaging Moesia until they were defeated near Adrianople in 587. To the Byzantines, it must have seemed like a reprise of the Hunnic aggression of the fifth century. (76)
Avar Conquest
With Sirmium now taken and operating efficiently from The Ring, Bayan I continued his conquests. Christoph Baumer writes how Bayan I drove his armies into the Balkans and demanded tribute from the Eastern Empire for peace and then, "together with the beaten Slavs, whom they abused as a kind of 'cannon fodder', the invaded Greece in the 580s" (Volume II, 208). They operated in warfare with tactics similar to those used by the Huns a century before. Like the Huns, the Avars were expert horsemen. Baumer notes that "The iron stirrup came to Europe only with the invading Avars in the second half of the sixth century." The stirrup "enabled riding in a squatting or almost standing position, which improved the rider's mobility, but also increased the impact of an attacking cavalry" (Volume I, 86). The stirrup greatly enhanced the already formidable Avar cavalry and made them the most feared and invincible mounted military force since the Huns. Baumer writes:
In his famous military handbook Strategikon, the Byzantine emperor Maurice (reigned 582-602) aptly described the battle style of the Avars, whom he compared to the Huns, as follows: `they prefer battles fought at long range, ambushes, encircling their adversaries, simulated retreats and sudden returns, and wedge-shaped formations...When they make their enemies take to flight, they are not content, as the Persians and the Romans, and other peoples, with pursuing them a reasonable distance and plundering their goods, but they do not let up at all until they have achieved the complete destruction of their enemies...If the battle turns out well, do not be hasty in pursuing the enemy or behave carelessly. For this nation [the steppe nomads] does not, as other do, give up the struggle when worsened in the first battle. But until their strength gives out, they try all sorts of ways to assail their enemies. (Volume I, 265-267)
Justin II had begun a war against the Sassanian Empire in 572 CE and, with imperial forces drawn to the east, Bayan I invaded further into Byzantine territories. He demanded higher and even higher tribute and defeated the imperial armies sent against him. It was not until 592 CE, with the conclusion of the empire's war with the Sassanids, that the emperor Maurice was able to send an army of adequate force against Bayan I. The Avars were driven from the Balkans and back into Pannonia by the imperial troops under the general Priscus, almost to their capital. The Avars would most likely have been destroyed en masse were it not for the insurrection in Constantinople known as Phocas' Rebellion in 602 CE.
At this same time, a plague broke out in the Balkans and swept across the surrounding regions. It is likely that Bayan I was one of the many victims of the disease. The historian H.H. Howorth, esq, notes:
We do not read again of Bayan, and it would appear that he died about this time, perhaps from the pestilence already named. It is not impossible that it was that pestilence, and the loss of their great leader, which made it possible for Priscus to win his victories so easily...The Avars never again recovered the vast power which they exercised under Bayan, who must be classed among the most successful of generals and the most powerful of rulers. (777)
Bayan I was succeeded by his son who attempted to carry on his father's empire. In 626 CE he led a campaign against Constantinople, allied with the Sassanids, in a land and sea attack. The formidable defenses of the Theodosian Walls (built under the reign of Theodosius II, 408-450) repelled the land attack while the Byzantine fleet defeated the naval assault, sinking many of the Avar ships. The campaign was a complete failure and the surviving Avars returned home to Pannonia. As Howorth notes, the Avars would never again wield the kind of military and political power they had under the leadership of Bayan I. Like Attila, his commanding personality and military brilliance would not live on in his sons. After 630 CE the Avar Empire began to decline and was finally conquered by Charlemagne of the Franks in 796 CE with relative ease. In essence, the Avar Empire began and ended with Bayan I.






