Search
Remove Ads
Advertisement
Summary 
Loading AI-generated summary based on World History Encyclopedia articles ...
Search Results

Article
Egyptian Gods - The Complete List
The gods and goddesses of Ancient Egypt were an integral part of the people's everyday lives for over 3,000 years. There were over 2,000 deities in the Egyptian pantheon, many whose names are well known - Isis, Osiris, Horus, Amun, Ra, Hathor...

Article
Chaucer's The Book of the Duchess Full Text & Summary
The Book of the Duchess is the first major work of the English poet Geoffrey Chaucer (l. c. 1343-1400 CE), best known for his masterpiece The Canterbury Tales, composed in the last twelve years of his life and left unfinished at his death...

Article
The Life of Diogenes of Sinope in Diogenes Laertius
Diogenes of Sinope (c. 404-323 BCE) was a Greek Cynic philosopher best known for holding a lantern to the faces of the citizens of Athens claiming he was searching for an honest man. He was most likely a student of the philosopher Antisthenes...

Article
The Mesopotamian Pantheon
The gods of the Mesopotamian region were not uniform in name, power, provenance or status in the hierarchy. Mesopotamian culture varied from region to region and, because of this, Marduk should not be regarded as King of the Gods in the same...

Article
Hesiod on the Birth of the Gods
The Greek poet Hesiod (c. 700 BCE) is most famous for his works Theogony and Works and Days. In this passage from Theogony, Hesiod relates the birth of the gods from cosmic Chaos and follows the lineage through the great Zeus, King of the...

Article
The Mayan Pantheon: The Many Gods of the Maya
The pantheon of the Maya is a vast collection of deities worshipped throughout the regions of Yucatan, Quintana Roo, Campeche, Tabasco, and Chiapas in Mexico and southward through Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador and Honduras. These gods informed...

Article
Diodorus Siculus' Account of the Life of Semiramis
Semiramis is the semi-divine Warrior-Queen of Assyria, whose reign is most clearly documented by the Greek historian Diodorus Siculus (l. 90-30 BCE) in his great work Bibliotheca Historica ("Historical Library") written over thirty years...

Article
Enuma Elish - The Babylonian Epic of Creation - Full Text
The Enuma Elish (also known as The Seven Tablets of Creation) is the Babylonian creation myth whose title is derived from the opening lines of the piece, "When on High". The myth tells the story of the great god Marduk's victory over the...

Article
The Shield of Heracles: The Complete Poem
The Shield of Heracles (also known as The Shield of Herakles and, in the original, Aspis Herakleous) is a poem of 480 hexameter lines written by an unknown Greek poet in the style of Hesiod (lived 8th century BCE). It deals with the Greek...
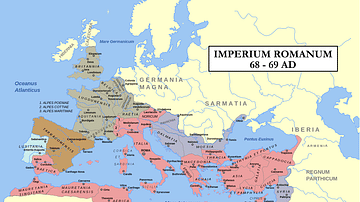
Article
The Batavian Revolt
Batavian revolt was a rebellion of the Batavians against the Romans in 69-70 CE. After initial successes by their commander Julius Civilis, the Batavians were ultimately defeated by the Roman general Quintus Petillius Cerialis. The year...