Pegasus (or Pegasos) is a winged-horse from Greek mythology which was fathered by Poseidon and was born from the severed neck of the gorgon Medusa, slain by Perseus. At the same time and in the same way, Chryasor was also born. Poseidon gave Pegasus to his son Bellerophon who put Pegasus to good use in his famous battle with the Chimaera.
The myth of Bellerophon begins with the hero visiting Tiryns and enjoying the hospitality of the city's king Proitos. However, trouble started when Stheneboia, the king's wife, fell in love with the hero and made inappropriate advances. Bellerophon, being a good guest, politely rejected these advances but predictably, Stheneboia saw red and went before the king and accused the visitor of attempting to seduce her. In punishment, Bellerophon was sent by Proitos to serve his father-in-law Iobates, King of Lykia. On arrival, Bellerophon was set a series of dangerous and impossibly difficult tasks, chief amongst them being to destroy the fearsome and rather bizarre Chimaera. This fire-breathing creature was a terrible mix of a lion's body with a snake for a tail and the head of a goat sprouting from its back. To aid him in this task, Bellerophon was fortunate to have at his disposal Pegasus. In some accounts he found the horse at the fountain of Pirene near Corinth, and Hesiod suggests this fact explains the name Pegasus, derived from 'water'- pēgē. Taming the horse with the help of Athena, Bellerophon rode (and flew) Pegasus and managed to kill the monstrous Chimaera with his spear.
Bellerophon and Pegasus went on to enjoy further success with other challenges Iobates set the hero including a battle with the Amazons. However, becoming rather boastful and thinking he could fly high enough on his winged steed to take his place amongst the immortal gods, Bellerophon was thrown by Pegasus and fell unceremoniously back to earth. Meanwhile, Pegasus kept on going and on reaching Mt. Olympus, he was given to Eos who was responsible for bringing Dawn across the sky each day. According to Hesiod in his Theogony, Pegasus also brought Zeus his thunder and lightning whenever needed.
Pegasus is also credited with creating a number of springs with a stamp of his hoof. Most famous of these were the Hippocrene spring on Mt. Helicon, close to the grove sacred to the Muses, and the spring at Troezen.
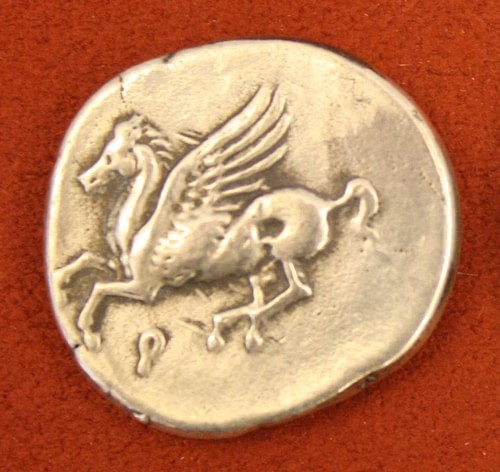
Pegasus appeared on Greek pottery, the earliest being Corinthian wares from the 7th century BCE. Pegasus was also a popular design on coins, in particular from Corinth from the 6th century BCE. A famous representation in sculpture is from the pediment of the Temple of Artemis on Corcyra (c. 580 BCE). The Bellerophon and Pegasus myth was also a popular subject in Roman art - especially engraved semi-precious stone cameos and floor mosaics - where the horse became symbolic of immortality.