The history of the alphabet started in ancient Egypt. By 2700 BCE Egyptian writing had a set of some 22 hieroglyphs to represent syllables that begin with a single consonant of their language, plus a vowel (or no vowel) to be supplied by the native speaker. These glyphs were used as pronunciation guides for logograms, to write grammatical inflections, and, later, to transcribe loan words and foreign names.
However, although seemingly alphabetic in nature, the original Egyptian uniliterals were not a system and were never used by themselves to encode Egyptian speech. In the Middle Bronze Age an apparently "alphabetic" system known as the Proto-Sinaitic script is thought by some to have been developed in central Egypt around 1700 BCE for or by Semitic workers, but only one of these early writings has been deciphered and their exact nature remains open to interpretation. Based on letter appearances and names, it is believed to be based on Egyptian hieroglyphs.
This script eventually developed into the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, which in turn was refined into the Phoenician alphabet. It also developed into the South Arabian alphabet, from which the Ge'ez alphabet (an abugida) is descended. Note that the scripts mentioned above are not considered proper alphabets, as they all lack characters representing vowels. These early vowelless alphabets are called abjads and still exist in scripts such as Arabic, Hebrew, and Syriac.
Phoenician was the first major phonemic script. In contrast to two other widely used writing systems at the time, cuneiform and Egyptian hieroglyphs, it contained only about two dozen distinct letters, making it a script simple enough for common traders to learn. Another advantage of Phoenician was that it could be used to write down many different languages since it recorded words phonemically.
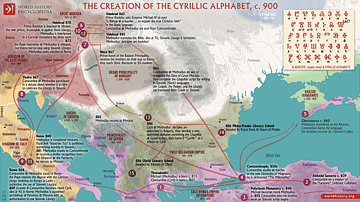
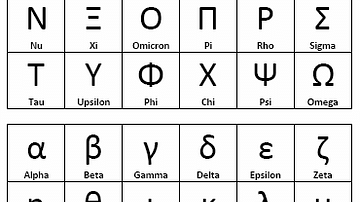
Phoenician colonization allowed the script to be spread across the Mediterranean. In Greece, the script was modified to add the vowels, giving rise to the first true alphabet. The Greeks took letters which did not represent sounds that existed in Greek and changed them to represent the vowels. This marks the creation of a "true" alphabet, with both vowels and consonants as explicit symbols in a single script. In its early years, there were many variants of the Greek alphabet, a situation which caused many different alphabets to evolve from it.
The Cumae form of the Greek alphabet was carried over by Greek colonists from Euboea to the Italian peninsula, where it gave rise to a variety of alphabets used to inscribe the Italic languages. One of these became the Latin alphabet, which was spread across Europe as the Romans expanded their empire. Even after the fall of the Roman Empire, the alphabet survived in intellectual and religious works. It eventually became used for the descendant languages of Latin (the Romance languages) and then for the other languages of Europe.