At the Battle of Teutoburg Forest (aka Battle of Varus), c. 9 CE, a combined force of Germans annihilated a Roman army consisting of three legions including three squadrons of cavalry and six cohorts of auxiliary troops. As some soldiers must have been left behind to defend summer camps, the army probably held 10,000 to 15,000 men or roughly 8 to10 % of the total Roman army. The sources do not mention the size of the German army at the famous battle. Based on the size of the catchment area, and the fact that Arminius, leader of the German forces, was not able to recruit all chieftains, it is likely that the Germans were heavily outnumbered, perhaps 1:2.
Seven years after the battle, the Romans sent Germanicus to revenge their fallen comrades by devastating the countryside. Nevertheless, the battle had a decisive impact in the long run; the Romans never consolidated the hold of Germania Interior, the land east of the Rhine. Instead, the Roman frontier (limes) along the Rhine was consolidated. Later, after the 16th century CE, the battle fed the imagination of countless military commanders and their belief in what a decisive battle might ensure in terms of glory and political gains

Prologue
Every youngster, who has ever studied Latin, has been met with the task of reading one of the great military historical works, The Gallic Wars by Julius Caesar. As such they have also read how Caesar c. 55 BCE built two bridges across the river Rhine and led his army across in order to confront the Germans on their home turf for the first time. In the next 60 years, this led to widespread warfare in the northwestern part of present Germany in the region between the Rhine and Weser rivers, with skirmishes penetrating as far as the river Elbe. Exactly how far into the interior (Germania Interior) the Romans succeeded in pressing forward is debated. The remains, however, of several Roman encampments, recorded archaeologically as far inland as the Roman fort at Barkhausen in Porta Westfalica, indicate how far the Romans reached under the leadership of Tiberius 9-7 BCE. By all accounts, the Romans afterwards settled down to colonise and Romanise the region.
Commanders
For this purpose, Publius Quinctilius Varus was appointed governor of Germania in 7 CE. At his command were three legions. In September 9 CE Varus broke up from his summer camp in order to march his army to winter in either Xanten or Mainz. History later tells us that Varus received intelligence from Arminius that a rebellion was cooking to the east of the Rhine. Arminius was son of a prominent Germanic chieftain, but had spent his childhood in Rome as a hostage. Here, he had received a military education as well as obtained Roman citizenship. In this capacity, he had obtained the rank of equestrian, as well as a post as squadron leader in Varus' army. Afterwards it became apparent that, Arminius – while serving as liaison between the Romans and the Germans - had plotted against the Romans, recruiting support and soldiers from a number of German chieftains.
We know from the archaeological excavations at Kalkriese that the attack had been carefully prepared during the summer. Thus, Arminius was not leading a random rebellion, but an ingeniously planned attack on the Roman army stationed along the Lower Rhine. Come September, Roman historians tell us that when Arminius had fed Varus the false information, Varus was lured to make a detour into Arminius' preselected and prepared battlefield. Historians also tell us that Segestes, the Roman father-in-law of Arminius, forewarned Varus; unfortunately, the Roman commander disregarded this and marched his legions towards total annihilation.
Battlefield Location
Although the story of the battle of Teutoburg was known since Antiquity, it was not accorded special significance until 1470 CE when the description by Tacitus was discovered and printed in Venice for the first time. However, the exact location of the battlefield continued to be an enigma for more than 500 years, until the amateur archaeologist, major Tony Clunn, after a successful day with his metal detector, hooked up with the leading archaeologist in Osnabrück, Wolfgang Schlüter. Based on the writing of the 19th-century CE historian Theodor Mommsen they began systematically to investigate an area north of the Wiehen Hills (Wiehengebirge) in Lower Saxony, Germany; more precisely at Kalkriese. Formerly, the area had been considered an archaeological desert because peasants had used a special technique when farming the land. In order to fertilise their fields, they would cut bricks of peat or grass to use as bedding for cattle in winter. Come spring, this manure would be spread out on the fields, which would be intensively worked as in-fields, creating layer upon layer of so-called podzoll or plaggen soil. This meant that the Roman landscape was covered with sometimes more than a meter to a meter and a half of agricultural soil. Until the introduction of deep ploughing, farmers might recover the odd coin, but no more. After WW2 this changed and a better sense of the Iron Age landscape gradually emerged.
Today, we know that the landscape was indeed covered with settlements, hamlets and small villages. At the same time, more and more coins were recovered, puzzling archaeologists and historians. How come, all these coins were found and, moreover, were datable to the period of Varus' governorship? When metal-detectors also discovered lead missiles, this led to the first archaeological excavations in 1989 CE. Today, very few archaeologists or historians doubt that the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest took place at a narrow stretch of land between the moors up north and the hilly and forested countryside to the south.
Tactics
It is generally believed that Varus was leading his army west. This is based on the distribution of archaeological finds, which tells a story of a slowly disintegrating army moving in this direction. When he reached the Wiehen Hills, he was obliged to skirt the hilly ridge to the south-west and the damp and intractable moors to the north. Looking at a map it is easy to see how the landscape literally pressed him into stretching out the line of march. Archaeology has shown that the attack took place along a narrow path covering approximately 15 - 20 km. and took the form of a battle in defile. It is generally believed that German warriors, hidden in the forest, initially attacked the rear end and the flanks of the Roman army from above by pelting the men with lances and lead missiles. These tactics basically hindered the Romans in taking up their classic battle formations. Also, it is probable that the seasoned soldiers became intermingled with the fleeing auxiliary troops making the Germanic force's attack strategy gradually easier. Finally, it may be worth speculating whether this form of warfare also better suited an army which probably consisted of diverse bands of brothers, each led by their own war-leader or chieftain. By deploying his troops as separate guerrilla bands, Arminius was perhaps able to forge a united front without risking internal strife.
Further down the line, at Oberesch, the Germans had erected a 400-meter long defensive rampart prior to the battle. Zigzagging through the landscape it resembles a post-medieval bastion. With drainage behind and a palisade in front, it attests to the careful planning and preparations which Arminius and his fellow chieftains had invested in the ambush.
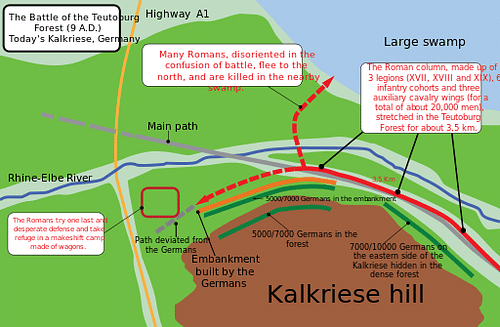
Here a more intense battle seems to have taken place as the German warriors led by Arminius went in for the final kill. However, continued archaeological excavations in the area make it likely that our knowledge of how the exact operation played out, will lead to new conclusions. One element, though, is hardly likely to be substantiated. Tacitus reported that one of the reasons why the Germans won the day was that the Roman bowstrings were soaked in rain and hence this weapon was rendered useless.
Weapons
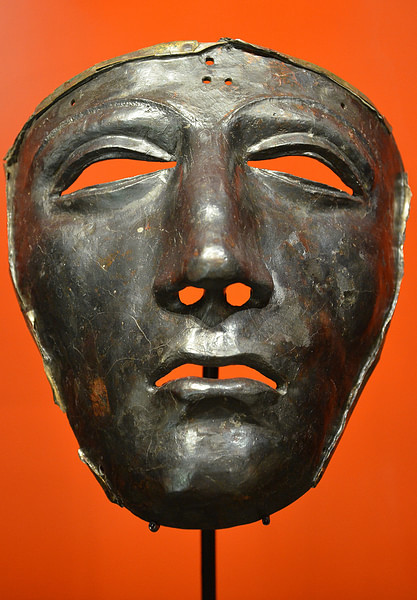
Archaeological excavations at the site have uncovered more than 1500 Roman coins and 6000 finds; nearly all of them are fragmented pieces of Roman military equipment like hobnails, pieces of ringmail shirts, belts, aprons, and brooches as well as fragments of auxiliary equipment. It is obvious, too, that the Germanic warriors carefully sifted the remains for anything useful. Thus, only one fragment of a Roman sword blade was found, while numerous scabbards had been discarded after being stripped of metal. This fate was also met by an impressive collection of shields, carefully stripped of bosses and other metal. These acts indicate that the German warriors preferred other types of weapons – their special shields and different swords (the spatha). It is highly likely that the short Roman swords (gladius hispaniensis) and their javelins (pila) found on the battlefield would have been scrapped and the metal reused by Germanic weapon smiths. One special find has become iconic for the battlefield at Kalkriese, the silver face mask of a Roman equestrian officer. Apparently part of the rampart fell upon it and some other gear hiding this from the sight of the post-battle looters and preserving it for us.
Aftermath
As later reported by ancient historians, the battle ended in the total annihilation of the Roman soldiers. Varus was said to have fallen on his own sword, while the victors kept the prized eagles of the Roman legions as visible signs of the triumph. Only two of those were ever recovered and that after seven years. The numbers of the legions were never reused in commemoration of the lost legions. No wonder, Suetonius reports to us that Augustus cried out and banged his head against a door when he received news of the defeat:
He suffered but two severe and ignominious defeats, those of Lollius and Varus, both of which were in Germany. Of these, the former was more humiliating than serious, but the latter was almost fatal since three legions were cut to pieces with their general, his lieutenants, and all the auxiliaries. When the news of this came, he ordered that watch be kept by night throughout the city, to prevent the outbreak, and prolonged the terms of the governors of the provinces, that the allies might be held to their allegiance by experienced men with whom they were acquainted. He also vowed great games to Jupiter Optimus Maximus, in case the condition of the commonwealth should improve, a thing which had been done in the Cimbric and Marsic wars. In fact, they say that he was so greatly affected that for several months in succession he cut neither his beard nor his hair, and sometimes he would dash his head against a door, crying: "Quintilius Varus, give me back my legions!" And he observed the day of the disaster each year as one of sorrow and mourning. (The Lives of the Twelve Caesars - Augustus, 23.1-3)
Five years later, the Roman Senate appointed Germanicus commander of the forces in Germania Interior. This led to a campaign 14 -16 EC during which he succeeded in meting out terrible revenge on the Germans, seriously routing the army of Arminius and regaining two of the three lost eagles. He also achieved some sort of healing of the trauma by securing the burial of the Roman soldiers, whose corpses had been left to rot on the battlefield. Tacitus writes that when the Roman commander, Germanicus, visited the place of battle, he commanded the physical remains of the soldiers should be collected and buried in pits. Archaeologists have shown that the bones and skulls found in these pits had been lying around uncovered for several years. This fits well with this report. However, Germanicus was not able to convert these victories into lasting domination of the region.
A Decisive Battle?
In the 19th and 20th centuries CE, historians generally believed that the Battle of Teutoburg Forest was decisive for the future history of Europe. At the battle, the Romans were dealt a terrible blow, after which they were forcefully driven back across the Rhine. Although the regions on both sides of this river operated as one frontier region, the military border kept the Romans on one side and the Germans on the other, until the Franks under Clovis effectively came to rule all the way to the Elbe.
Later historians have of course questioned this. In their opinion, it was, from an economic point of view, not advantageous to subjugate what was basically a rural hinterland of no particular interest. It was simply better to establish sensible and safe trading relations with the Germania interior rather than to invest money and men including formally these former provinces into a now sprawling empire reaching all the way to Hadrian's Wall. The border along the Rhine was simply easier and thus also cheaper to defend in depth. Also, it served as a powerful magnet for men from the Germania interior wishing to be recruited into the Roman army. It is probable that the only reason the battle at Teutoburg was remembered so vividly had to do with the fact that it was such a devastating and humbling defeat that it hit the public military reputation of the Romans so hard. If you rule and manage by terror, a devastating defeat at the hands of an enemy may well cost you dearly, when you turn to confront the next rebel down the line.
An Iconic Battle?
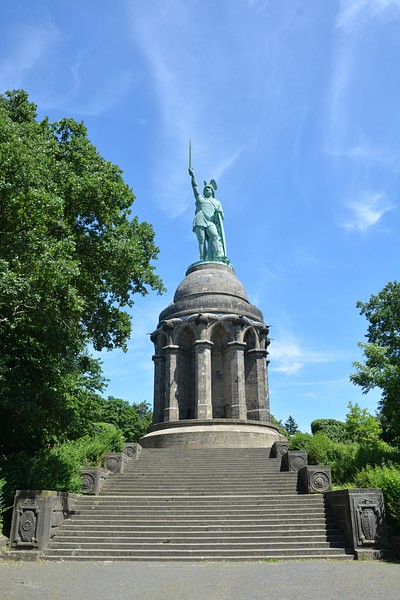
However, the aura of the Battle at Teutoburg had a second life after the Reformation in the 16th century CE, when the works of Tacitus came to inspire the Germans seeking liberation from the Catholic church to use Arminius (aka Hermann, as he was now called) as the champion of the people par excellence. Later this idea took off when he was turned into the champion of the German people against the Varus of all times, Napoleon. As the Romantics envisioned it through paintings, poetry, and plays, General Blücher was simply Arminius reborn, while Napoleon was the Roman general routed at Waterloo. At this point, Germans began to plan for a serious monument, the Hermann Monument near Detmold (where the battle at that time was believed to have taken place). Nevertheless, it was not until 1875 CE the Hermanns Denkmal was erected: 57.4 meters high the monument continues to raise its sword pointing westward. Measuring seven meters and 600 kg this was donated by the Krupp company. Today, it reminds us of the meticulous metallic scavenging, which went on at Kalkriese in September 9 CE. Following upon the astounding victory in 1871 the German elite thought more of it as a sign of what the inscription said: "German Unity under my Strength" (Deutsche Einigkeit Meine Staerke). On his head, Hermann carries a winged helmet, and at his foot lies a crushed Roman Eagle. The portrait of Hermann was forged out of metal scrapped from a French canon and melted into the portrait of the newly created German Emperor.
Paradoxically enough, though, this German veneration of Arminius as a national symbol of German unity, nevertheless, carried with it the seed of the ultimate destruction of the German army in WW2.
During the Middle Ages, most warfare consisted of an endless series of sieges followed by looting and occasional harrowing of the countryside. Pitched battles were occasionally fought, but in general kings and their military leaders sought to avoid them; costly and potentially devastating, most generals feared them. This changed fundamentally in the late 18th century CE when Napoleon entered the scene bolstering the idea that glory could indeed be won – and hence should be sought – in the magnificent set-piece battles, which he excelled in. As the Germans sought unity by waging war (1864 - 1871 CE) on their neighbours, Denmark, Austria and France, a gifted military leader, Helmuth von Moltke the Elder came forward. Inspired by Clausewitz (general and war theoretician), Moltke succeeded in both laying down the rulebook for how to wage war in the 19th century CE and win an impressive number of decisive battles in the manner of the greatest German hero of them all, Arminius.
Thus, even though history is witness to the fact that wars, in the end, are won by attrition and only very seldom in decisive battles, the gifted German generals in WW2 were challenged by the allure of battle. Of course, they might in this context be accused. On one hand, they felt they had to follow orders from a military incompetent; on the other hand, they rightly knew that any war which did not gain glories on the battlefield, could not be won by German forces, which in the long run would lack the essential manpower and resources to accomplish it by exerting suffering. In such a situation, it is understandable that luring the enemy into decisive battles might carry fruit. This was, therefore, the strategy, which in the end was behind the German decision to push forward into the Ardennes, and engage the Allied at the Battle of the Bulge December 1944 to January 1945 CE; arguably one of the last great battles in world military history.
Lurking behind this was thus the lure of the decisive battle, which the German generals believed their Arminius or Hermann aka Moltke had won in the Teutoburg Forests of yesteryear. Thanks to the archaeologists, we now have to speculate whether, in fact, Arminius did not rather fight his way through as a gifted leader of groups of guerrillas and warbands?
Museums
An important and very interesting museum is located on the famous battle site. This is of utmost importance for anyone wishing to understand the events leading up to the battle, how it was enacted and the historical and geographical context. It is a nice museum for children too. Outside the museum, visitors are invited on a tour through the battle site, which gives a fine indication of how it played out for the Roman soldiers and the German warriors
In the German Historical Museum in Berlin, the first exhibition is about the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. The curators obviously chose the mask carried by a Roman in battle as the starting point of what is fundamentally a very impressive exhibition in three parts catering for the sweeping history of the ups and downs of German nationalism, unification and divisions over 2000 years.











