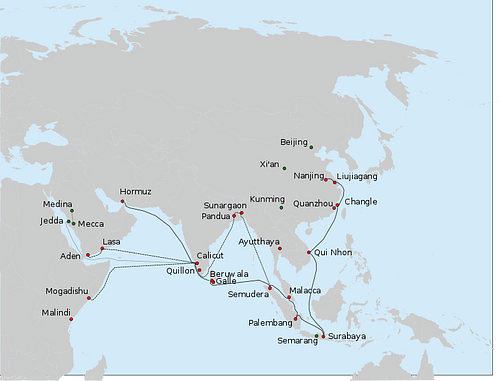
Admiral Zheng He (aka Cheng Ho, c. 1371-1433 CE) was a Chinese Muslim eunuch explorer who was sent by the Ming dynasty emperor Yongle (r. 1403-1424 CE) on seven diplomatic missions to increase trade and secure tribute from foreign powers. Between 1405 and 1433 CE Zheng He commanded huge fleets loaded with trade goods and high-value gifts to such far-flung places as Hormuz in the Persian Gulf and Mogadishu in East Africa. Following established sea routes but often finding himself the first ever Chinese person to land at many of his destinations, Zheng He is widely regarded as the greatest ever Chinese explorer. His travels may not have brought much success in terms of new trade or lasting tribute to the imperial court but the knowledge, ideas, and exotic goods he brought back home - from jewels to giraffes - created an interest in foreign countries and a realisation of their wealth which contributed to China's increased role in world trade in later centuries. Even if his wake was not immediately followed, Zheng He had shown the way.
Yongle Emperor's Foreign Policy
One of the enduring symbols of the Ming dynasty's eagerness to extend international relations under its third emperor, Yongle, is the seven sea voyages of Zheng He. Yongle's predecessors had been cautious to the point of isolationism when it came to foreign affairs, largely out of fear of military conquest by neighbouring peoples, especially the Mongols. More secure on his imperial throne, and having grabbed it in the first place after a three-year civil war, Yongle perhaps sought some international legitimacy for his position as emperor.
The traditional presentation of tribute to Chinese emperors by other, smaller states in Southeast Asia was given to prevent invasion or achieve a theoretical promise of protection in the case of invasion by a third party or because diplomatic missions giving that tribute were permitted to conduct trade while in China. The tribute, usually far less valuable than the goods which the emperors gave out, had always been a badge of approval to the Chinese, indicative that their emperor was indeed the Son of Heaven and the most powerful ruler on earth. It also confirmed the Chinese vanity that their own culture was superior to all others. The system had lapsed during the Mongol Yuan dynasty (1276-1368 CE) but Yongle wanted to revive it. What better way to convince the powerful officials of the imperial bureaucracy that he was the chosen one than having foreign ambassadors prostrate themselves in the Forbidden City and offer up a handsome sample of the riches of their country?
Another possible motive, at least for the earlier voyages to Southeast Asia, may have been to discover the whereabouts of the deposed emperor Jianwen (r. 1398-1402) and so ensure he did not stir up a rebellion to take back his throne from his usurper Yongle. The scale of the fleets involved has also led some scholars to suggest the expeditions were rather more interested in some form of colonialism than mere diplomacy and trade, but this view is not widely held.
Admiral Zheng He
Yongle would dispatch many diplomatic missions across land routes to such places as Samarkand and Tibet but the man selected to lead the emperor's most important maritime forays into foreign diplomacy was Zheng He. Born into a Muslim peasant family in Yunnan province in southern China c. 1371 CE, his family-given name was Ma Ho. The future explorer would have a difficult childhood but he certainly had the travel bug in his veins as his father had made the Hajj or pilgrimage to Mecca. Living in a region of China that was then controlled by the Mongols, Ma Ho was captured by Ming forces at the age of ten. In the typical treatment of those captured in warfare and destined to be slaves or servants, Ma Ho was castrated. He was then conscripted into the army commanded by a Ming prince, none other than the future emperor Yongle. Ma Ho's talents saw him progress through the ranks, being selected as the head eunuch and becoming an important support to Yongle's claim for the throne. When Yongle won a three-year civil war and became emperor in 1403 CE, Ma Ho was given the new name of Zeng He (aka Cheng Ho).
India & Sri Lanka
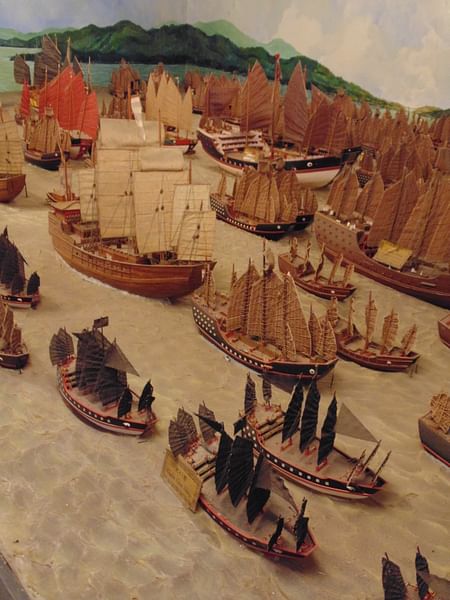
By 1405 CE Zheng He was an admiral in the imperial fleet, and he was selected by the emperor to lead a fleet across the Indian Ocean to explore the possibilities of new tributary states and bring them into the sphere of Chinese influence. The massive fleet of 317 ships had been under construction since 1403 CE and included 62 baochuan, then the largest ships in the world. These Chinese junks, also known as 'treasure ships', were perhaps up to 55 metres (180 ft) in length and 8.5 metres (28 ft) wide (although the exact dimensions are disputed amongst historians). The junks Zheng had in his fleet would not have been significantly different from those described as follows by the famed Muslim traveller from Tangier Ibn Battuta (1304 - c. 1368 CE):
The large ships have anything from twelve down to three sails made of bamboo rods plaited like mats. A ship carries a complement of a thousand men…The vessel has four decks and contains rooms, cabins and saloons for merchants.
(quoted in Brinkley, 170)
Many of the vessels, built at the shipyards of Nanjing, were equipped with such innovations as water-tight compartments, sternpost rudders, magnetic compasses and paper charts and maps. The ships were packed with fresh water, food supplies, and Chinese luxury goods intended to woo foreign rulers into displaying their appreciation of the Ming dynasty's obvious wealth and power by sending back to China their own riches in tribute. Goods shipped out included silk, tea, painted scrolls, gold and silver objects, textiles, carved and manufactured goods, and fine Ming porcelain. There was space, too, for a huge number of personnel: estimates range from 20,000 up to 32,000 expedition members on the first voyage. These included diplomats, medical officers, astrologers, ship's crews, and military personnel which, along with canons, bombs, and rockets, ensured the expedition could ably defend itself wherever it ventured.
The first three voyages of Zheng He (1404, 1408 and 1409 CE) followed more established trade routes. He went via Southeast Asia, sailing down the coast of Vietnam, stopping at Sumatra and Java and then on through the Malay Archipelago and through the Straits of Malacca, crossing the eastern Indian Ocean to reach India and Sri Lanka.
Wherever he landed, Zheng He led a delegation to the local ruler to whom he presented messages of goodwill and China's peaceful intentions towards them. He then presented a large quantity of gifts and invited the ruler to either come in person or send an ambassador to the court of Emperor Yongle. Many rulers took up the offer immediately and delegates were accommodated on Zheng He's ships to be eventually taken to China on the return voyage. Some rulers were not so keen, of course, notably Alagakkonara, the king of Sri Lanka, who turned out less than welcoming to these strange visitors and tried to plunder Zheng He's ships. Undeterred, Zheng He abducted the king and brought him in person back to the Chinese imperial court, where he was later released after promising to pay regular tributes, which he did do.
There were also secondary adventures besides securing new diplomatic ties. The return journey of the first expedition, for example, saw Zheng He capture the pirate Ch'en Tsu-i, who had caused havoc in the Malacca Straits and beyond, a feat which greatly enhanced the admiral's reputation in Southeast Asia. The second voyage on its return in 1408 CE successfully resolved a local dispute on Java. These and other actions only strengthened the view that China was the chief power in the region and its greatest source of stability.
Persian Gulf & Africa
Zheng He's fourth voyage in 1413 CE saw him sail to India again, once more pushing on around the southern tip of the subcontinent and visiting again Cochin and Calicut on the west coast. This time he also found time to stop off at the Maldive Islands, before crossing the Arabian Sea and reaching Hormuz on the Persian Gulf. Sailing down the coast of Arabia, he then went on to Aden and up the Red Sea to Jeddah, from where a party travelled to Mecca. A report states that 19 foreign rulers sent tributes and diplomatic missions to the emperor as a consequence of this fourth voyage.
Voyages five, six, and seven (1417, 1421, and 1431 CE) reached even further afield, landing at Mogadishu, Malindi, and Mombassa, all on the coast of East Africa. Zheng He is the first attested Chinese to visit the Swahili coast. The ruler of Mogadishu was responsive and did send an embassy to Yongle, and even distant Zanzibar was reached by Zheng He's fleet.
From Africa, Zheng He brought back such exotica as lions, leopards, camels, ostriches, rhinos, zebras, and giraffes. These animals caused wonder back in China, where the giraffe, for example, was considered living evidence of the qilin, a sort of Chinese unicorn which represented good fortune. There is a surviving painted silk scroll from the period showing a giraffe given to the emperor by King Saif Al-Din Hamzah Shah of Bengal. Besides animals, Zheng He also brought back gems, spices, medicines, and fine cotton cloth, as well as knowledge of strange foreign peoples and customs.

Zheng He, like many great explorers before and since, died in the middle of an expedition, his seventh voyage. The great admiral died in Calicut in 1433 CE, and his body was returned to China for burial in Nanjing. Zheng He had made an incredible series of journeys, as this inscription on a tablet he erected in 1432 CE in Fujian, China relates:
We have traversed more than one hundred thousand li (27,000 nautical miles) of immense waterspaces and have beheld in the ocean huge waves like mountains rising sky high, and we have set eyes on barbarian regions far away hidden in a blue transparency of light vapors, while our sails, loftily unfurled like clouds day and night, continued their course (as rapidly as) a star, traversing those savage waves as if we were treading a public thoroughfare…
(quoted in von Sivers, 406)
There would be no more great maritime expeditions as the Chinese closed the door on the outside world and returned to its isolationist foreign policy of old. One of Yongle's successors, Xuande (r. 1426-36 CE) had initially supported Zheng's continuing voyages but he eventually put an end to the costly expeditions. The emperor even went so far as to ban the construction of any ocean-going ships and prohibit those that existed from being used for voyages beyond Chinese coastal waters. The return to isolationism may have been due to the increased threat from the Mongols, and the huge expense of rebuilding parts of the Great Wall of China likely called for some cutbacks elsewhere. In any case, the original aim of the voyages - to secure foreign tribute - was largely unsuccessful outside of Southeast Asia. The expense of the expeditions and the goods they carried did not match the value of the tributes that came in return. Put simply, many foreign states, although interested in the trading possibilities, did not quite agree that China, the self-styled Middle Kingdom, was the centre of the world; a view confirmed by the opening up of the New World at the other end of the same century that Zheng He had begun his voyages.