The London Blitz (September 1940 to May 1941) was a sustained bombing campaign by the German Air Force during the Second World War (1939-45). Londoners were subjected to nightly bombings that killed thousands, destroyed homes, and necessitated long and uncomfortable nights spent in air raid shelters. This article tells the story of the Blitz through the eyes of those who experienced it firsthand.

After the fall of France in the early summer of 1940, the German Air Force (Luftwaffe) set itself the task of destroying the British Royal Air Force (RAF) both in the air and on the ground, a necessary prelude to an invasion. However, as the RAF began to win the Battle of Britain and so maintain air superiority, the Luftwaffe switched objectives to the bombing of cities, particularly London, in the hope of destroying civilian morale. Colonel Adolf Galand of Luftwaffe Jagdgruppe 26 explains this switch:
We didn't know at the time why he [Adolf Hitler] changed to London: we had only to obey orders. I believe today that Hitler and Göring wanted to make use of their advantage of having the capital of the enemy in the range of their fighters which could therefore escort the bombers. On the other side Berlin was far out of the effective range of the RAF at this time...Nobody knew at the time how much was needed to destroy a great part of the town. Perhaps Hitler and Göring hoped that they would force England to negotiate after these attacks.
(Holmes, 138)
Peter Stahl, a crew member of a Junkers Ju 88, noted in his diary his experience of bombing London in one of the first raids in early September 1940:
It must be terrible down there. We can see many conflagrations caused by previous bombing raids. The effect of our own attack is an enormous cloud of smoke and dust that shoots up into the sky like a broad moving strip.
(Holland, 731)
On the ground, F. W. Hurd, a member of the Auxiliary Fire Service (AFS), describes the sound of a bomb dropping close to him when fighting a fire in a London gasworks:
Guns started firing, and then I had my first experience of a bomb explosion. A weird whistling sound and I ducked behind the pump with the other two members of the crew. The others, scattered as we were, had thrown themselves down wherever they happened to be. Then a vivid flash of flame, a column of earth and debris flying into the air and the ground heaved. I was thrown violently against the side of the appliance…what a sight. About a mile to our right was the river front. The whole horizon on that side was a sheet of flame. The entire docks were on fire! On all other sides it was much the same. Fire everywhere. The sky was a vivid orange glow…And all the time the whole area was being mercilessly bombed. The road shuddered with explosions. AA shells were bursting overhead…The shrapnel literally rained down. It was now about midnight and still the racket kept on. It surprised me how quickly one got used to sensing whether a bomb was coming our way or not.
(Gardiner, 15-16)
Bombs landed on all sorts of places, but it was local landmarks being destroyed that often shocked the most, as explained by Anthony Heap, a local government official:
I heard that Tussaud's cinema caught a packet last night. So as soon as the All Clear went at 6.25 I dashed along to see. And by gosh it had too. Only the front of it in Marylebone Road and the proscenium was left standing. The rest was completely demolished as were some buildings behind it as well…not a single window in any building in the vicinity remained intact. Huge crowds thronged along the Marylebone Road to see the ruins. It was one of the sights of London today.
(Gardiner, 44)
Londoners went on with their daily lives as best they could, as explained here by Phyllis Warner:
One of the oddest things about our everyday life is its a mixture of ruthless horror and every-day routine. I pick my way to work past the bomb craters and the shattered glass, and sit at my desk in a room with a large hole in the roof (a block of paving stone came through). Next to a house reduced to matchwood, housewives are giving prosaic orders to the baker and the milkman. Of course, ordinary life must go on, but the effect is fantastic. Nobody seems to mind the day raids. It is the nights which are like a continuous nightmare, from which there is no merciful awakening. Yet people won't move away. I know that I'm a fool to go on sleeping in Central London which gets plastered every night, but I feel that if others can stand it, so can I.
(Gardiner, 48)
Sometimes people had no time to seek shelter, as told here by an anonymous East Ender:
The day I was hit was October 13th, 1940. About ten to eight I said to my wife and my in-laws, 'Well, I'll be off now,' and I just walked out the door. Lovely, big three-floor houses they were and I just walked up the approach road about twenty yards from the church which was our air-raid post and suddenly there was – shh – nothing. I heard nothing and I fell flat on my face. I picked myself up, I turned around and all I could see was just a grey curtain hanging down the middle of the road, about twice as wide as this pub. It was just a brownish-grey curtain hanging there and I thought, My God, something's happened. So I staggered down to the post and I said to the post warden, 'Jim, I think something's happened up at the Prince of Wales.' When we went up there and when I saw it I said, 'Christ almighty, the family's down there!' And there it was – we were there, about fourteen of us all on this big row of houses, and it was just one bloody great hole.
(Holmes, 140-1)
The authorities took some months to build communal shelters and then make sure they were not themselves unhealthy death traps. Barbara Nixon, an Air Raid Precaution (ARP) volunteer, describes the poor state of shelters in her district in Finsbury:
They were poorly ventilated, and only two out of nine that came in my province could pretend to be dry. Some leaked through the roof and umbrellas had to be used; in others the mouth of the sump-hole near the door had been made higher than the floor, and on a rainy night it invariably overflowed to a depth of two inches at one end decreasing to a quarter of an inch at the other, and rheumaticky old ladies had to sit upright on their benches for six to twelve hours on end, with their feet propped up on a couple of bricks. four or five times during the night we used to go round with a saucepan and bucket baling out the stinking water…There were chemical closets usually partially screened off by a canvas curtain. But even so, the supervision of the cleaning of these was not adequate. Sometimes they would be left untended for days on end and would overflow on to the floor…Then there was the question of lights…We had one hurricane lamp for about fifty people…The one paraffin light was the only heating that there was in those days. It was bitterly cold that winter.
(Gardiner, 62)
A shelter was not a guarantee of safety. Margaret Turpin recalls the night her shelter was hit by a bomb when she and her family found themselves buried in rubble:
I must have had lots of periods of unconsciousness…I remember seeing an ARP helmet, and it was way, way up, a long way away. And then suddenly it was quite near. I do remember the man saying to me, 'We'll soon have you out.' He said, 'All we've got to do is get your arm out.' And I looked at this arm that was sticking out of the debris, and I said, 'That's not my arm,' and he said, 'Yes it is love, it's got the same coat'…and I don't remember coming out of the shelter. I do remember being in the ambulance, and I think for me that was probably the worst part…I felt somebody's blood was dripping on me from above, and I found that awful - mainly I think because I didn't know whose blood it was, whether it was someone I knew and loved or not. And I tried to move my head, but of course it was a narrow space and I couldn't get my head away from the blood. And I heard a long time afterwards that the man was already dead. But it couldn't have been my father because he was taken out of the shelter and he didn't die till two days later…He died, my mother died, my baby sister died, my younger sister died. I had two aunts and they died, an uncle died…I knew almost immediately because when I came home from hospital…there were milk bottles outside and I just knew then that nobody had come home to take them in…The seven were all buried on the same day. My brother said that they put Union Jacks on the coffins…They sent me to Harefield…But unfortunately the people at Harefield could see the raids on London, and they used to come out to watch, to view it like a spectacle, and I couldn't stand that.
(Gardiner, 64-5)
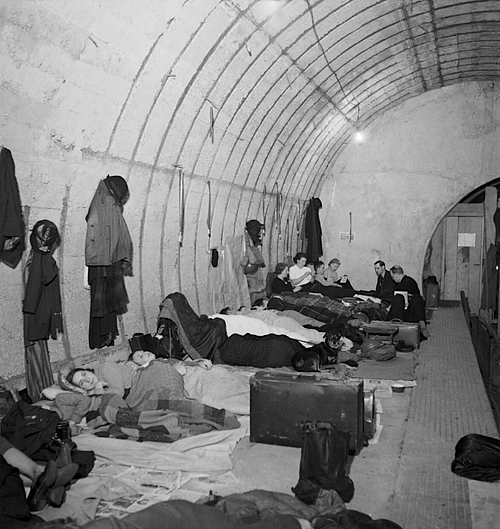

The stations of the London Underground were a popular refuge, with people sleeping on the platforms in rows. A journalist describes the scene in the Elephant and Castle station:
From the platforms to the entrance the whole station was one incumbent mass of humanity…most of this mass of sleeping humanity slept as though they were between silken sheets. On the platform when the train came in, it had to be stopped in the tunnel while police and porters went along pushing in the feet and arms which overhung the line. The sleepers hardly stirred as the train rumbled slowly in. On the train I sat opposite a pilot on leave. 'It's the same all the way along,' was all he said.
(Gardiner, 84)
Some families preferred to stay near their homes, and so they erected an Anderson shelter in their garden. Made of sheet metal and packed around with soil, they could resist close calls and flying debris but not, of course, a direct hit. A London air raid warden, Mr Butler describes one tragedy where the Anderson shelter survived but not the occupant:
There was an Anderson shelter and apparently there was a little girl inside. Her parents had gone round the corner to visit their friends or relations or something and the shelter was more or less caved in and covered with soil. I got down into the shelter and there was this little girl about fifteen or sixteen and her mouth was full of soil. Naturally, I got hold of her hand, which is our job to console these people and try to quieten them down. She was in a pretty bad state and I cleaned her mouth out; she laid back and as she was catching her breath, sort of breathing heavily, some stupid devil walked over the top of the shelter, soil came down and went back in this girl's throat and as she squeezed my hand like that she just faded out. Now I had the feel of that girl clenching my hand for weeks and weeks and weeks. I could never forget it and I don't forget it now.
(Holmes, 144)
One family that stayed at home was the Royal Family, who earned much respect for remaining at Buckingham Palace. When the palace was slightly damaged on 13 September 1940, Queen Elizabeth was not too distressed:
I'm glad we've been bombed. Now I feel we can look the East End in the face.
(Ziegler, 121)
The government was keen to keep tabs on people down in the shelters and find out if any social unrest could be bubbling under the surface. There was a Mass-Observation unit that sent out secret observers who then compiled reports on the public's behaviour. Mostly there ended up next to nothing to report beyond rumours as to what some couples were getting up to in the darker corners or the existence of a black market in getting the best positions to sleep in. One mundane report is typical, the highlight being a little aggravation between understandably stressed family members:
First was a girl, shouting and screaming at her mother. In the end they were separated by force, and led away from each other, struggling and screaming. The other case was of a man and his wife. The wife wanted him to sit down, the husband wanted to walk about. She became very excited, and a crowd of 'rubberers' formed round them. She bit his ear and tore out his hair. He smacked her face and threw her to the ground.
(Levine, 88).
The number of homeless kept on rising, and the need to look after them inspired such organisations as the Women's Voluntary Service (WVS), as here remembered by an anonymous East Ender:
A big morale booster was the Women's Voluntary Service – the WVS…When the Blitz started they certainly proved their worth. They went out with mobile canteens right in the middle of the Blitz; the following day they had their clothing centres open. People who had lost everything were fitted up with clothes and then taken along by the WVS and be given a cup of tea and a bun, then taken along to the assistance people who doled them out £10 or £20, whatever the size of the family was.
(Holmes, 142)

Tragedies were everywhere as people lost much more than their property. Frances Faviell, a Red Cross nurse in London recalls one woman's grief:
There was a little woman from Dovehouse Street sitting on a bench…Dovehouse Street had had a parachute mine on it and the Chelsea Hospital for Women had dealt with many casualties. Suddenly her control gave way and she began screaming in a frenzy of grief…'He's gone…He's gone and I'm all alone and no home, nothing. No one wants me…Why didn't I go with him, it's cruel, it's cruel, cruel. Why? Why?' Her anguish was terrible.
In the appalled silence with which officialdom treats such outbursts – almost as if she had said or done something obscene – a sleek, well-dressed clergyman…told her sternly to desist – that what had happened was God's will and that she must accept it and thank Him for her own deliverance from death. She looked at him in dazed misery as if he spoke a foreign language and began screaming even more wildly. 'God! There's no God! There's only Hitler and the Devil'
(Gardiner, 317)
A spirit of defiance drove people on, as evidenced by this anecdote from Anthony Eden, then Foreign Secretary, who was with Wendell Wilkie, the US politician sent to determine the mood of Britain during the Blitz:
We were coming out of the Foreign Office [and] there was a man working at windows which had been broken in the night, on top of a ladder, and Wilkie went up to him and said, 'How do you feel about the war?' The man looked slightly astonished and said, 'What do you mean?' Wilkie said, 'Well do you want to go through with it,' and the man said 'Hitler ain't dead yet, is he?'…And that, Wilkie told me long after, was a view found throughout the country and therefore if Britain did hold on and did work her way through, immense credit of course to Winston [Churchill] and his leadership. But immense credit is also due to the British people, because it was their victory.
(Holmes, 147).
The 'Blitz spirit', the pulling together of strangers from different levels of society to defiantly resist the terrors of the bombing, was, for many, the defining experience of those dark days of 1940 and 1941. Much has been made in recent times of a 'myth' of the Blitz with undue emphasis given to rare incidents of social unrest, looting, and prejudices against perceived outsiders. The vast majority of eyewitnesses speak of people simply getting on with their lives as best they could in terrible circumstances. Another recurring theme in witness accounts is that people had an all too clear sensation that they were playing a role in a drama that would have consequences for the future of Europe. As Caryl Brahms noted in her diary in December 1940:
These are the days to be alive in. These days now. They are hard, unhappy, lonely, wasted, infuriating, terrifying, heartbreaking days. But they are history. And in them we are a part of history. We are lucky to be living now.
(Levine, 313)