In the following excerpt from his Library of History, Book XVI, chapter 14, the historian Diodorus Siculus (1st century BCE) chronicles the famous Battle of Chaeronia of 338 BCE, in which Phillip II of Macedon, his son Alexander and their allies defeated the Greek forces of Athens and Thebes resulting in the unification of the Greek city-states under Macedonian rule. As Alexander's contribution to the battle (he is traditionally credited with breaking the Theban lines and winning the battle) has been disputed, it is of interest to read an earlier historian's account of the battle.
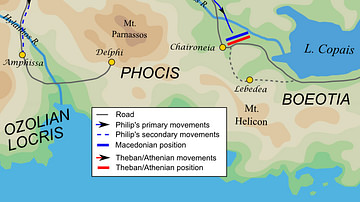
"In the year Charondas was first archon in Athens, Philip, King of Macedon, being already in alliance with many of the Greeks, made it his chief business to subdue the Athenians, and thereby with more ease control all Hellas. To this end he presently seized Elateia [a Phocian town commanding the mountain passes southward], in order to fall on the Athenians, imagining to overcome them with ease; since he conceived they were not at all ready for war, having so lately made peace with him. Upon the taking of Elateia, messengers hastened by night to Athens, informing the Athenians that the place was taken, and Philip was leading on his men in full force to invade Attica.
The Athenian magistrates in alarm had the trumpeters sound their warning all night, and the rumor spread with terrifying effect all through the city. At daybreak the people without waiting the usual call of the magistrate rushed to the assembly place. Thither came the officials with the messenger; and when they had announced their business, fear and silence filled the place, and none of the customary speakers had heart to say a word. Although the herald called on everybody "to declare their minds"—-as to what was to be done, yet none appeared; the people, therefore, in great terror cast their eyes on Demosthenes, who now arose, and bade them to be courageous, and forthwith to send envoys to Thebes to treat with the Boeotians to join in the defense of the common liberty; for there was no time (he said) to send an embassy for aid elsewhere, since Philip would probably invade Attica within two days, and seeing he must march through Boeotia, the only aid was to be looked for there.
The people approved of his advice, and a decree was voted that such an embassy should be sent. As the most eloquent man for the task, Demosthenes was pitched upon, and forthwith he hastened away [to Thebes. —-Despite past hostilities between Athens and Thebes, and the counter-arguments of Philip's envoys, Demosthenes persuaded Thebes and her Boeotian cities that their liberty as well as that of Athens was really at stake, and to join arms with the Athenians.] . . .When Philip could not prevail on the Boeotians to join him, he resolved to fight them both. To this end, after waiting for reinforcements, he invaded Boeotia with about thirty thousand foot and two thousand horse. . . .
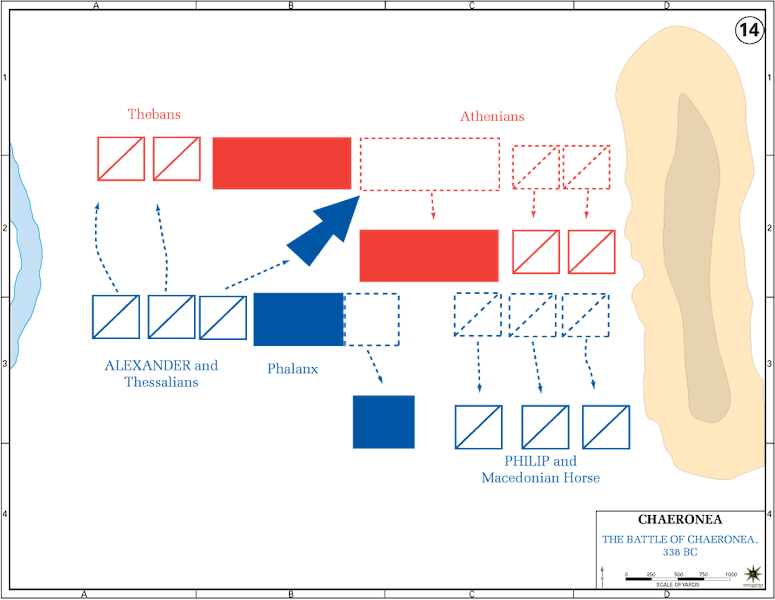
Both armies were now ready to engage; they were equal indeed in courage and personal valor, but in numbers and military experience a great advantage lay with the king. For he had fought many battles, gained most of them, and so learned much about war, but the best Athenian generals were now dead, and Chares—-the chief of them still remaining—-differed but little from a common hoplite in all that pertained to true generalship. About sunrise [at Chaeronea in Boeotia] the two armies arrayed themselves for battle. The king ordered his son Alexander, who had just become of age, yet already was giving clear signs of his martial spirit, to lead one wing, though joined to him were some of the best of his generals. Philip himself, with a picked corps, led the other wing, and arranged the various brigades at such posts as the occasion demanded. The Athenians drew up their army, leaving one part to the Boeotians, and leading the rest themselves.
At length the hosts engaged, and the battle was fierce and bloody. It continued long with fearful slaughter, but victory was uncertain, until Alexander, anxious to give his father proof of his valor—-and followed by a courageous band—-was the first to break through the main body of the enemy, directly opposing him, slaying many; and bore down all before him—-and his men, pressing on closely, cut to pieces the lines of the enemy; and after the ground had been piled with the dead, put the wing resisting him in flight. The king, too, at the head of his corps, fought with no less boldness and fury, that the glory of victory might not be attributed to his son. He forced the enemy resisting him also to give ground, and at length completely routed them, and so was the chief instrument of the victory.
Over one thousand Athenians fell, and two thousand were made prisoners. A great number of Boeotians, too, perished, and many more were captured by the enemy. . .
[After some boastful conduct by the king, thanks to the influence of Demades, an Athenian orator who had been captured], Philip sent ambassadors to Athens and renewed the peace with her [on very tolerable terms, leaving her most of her local liberties]. He also made peace with the Boeotians, but placed a garrison in Thebes. Having thus struck terror into the leading Greek states, he made it his chief effort to be chosen generalissimo of Greece. It being noised abroad that he would make war upon the Persians, on behalf of the Greeks, in order to avenge the impieties committed by them against the Greek gods, he presently won public favor over to his side throughout Greece. He was very liberal and courteous, also, to both private citizens and communities, and proclaimed to the cities that he wished to consult with them as to the common good.' Whereupon a general council [of the Greek cities] was convened at Corinth, where he declared his design of making war on the Persians, and the reasons he hoped for success; and therefore desired the Council to join him as allies in the war. At length he was created general of all Greece, with absolute power, and having made mighty preparations and assigned the contingents to be sent by each city, he returned to Macedonia where, soon after, he was murdered by Pausanius, a private enemy."