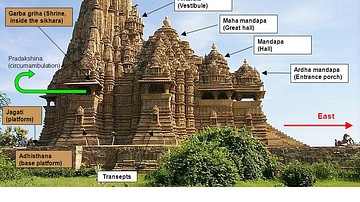
Adisthana - the decorative raised platform on which a temple is built.
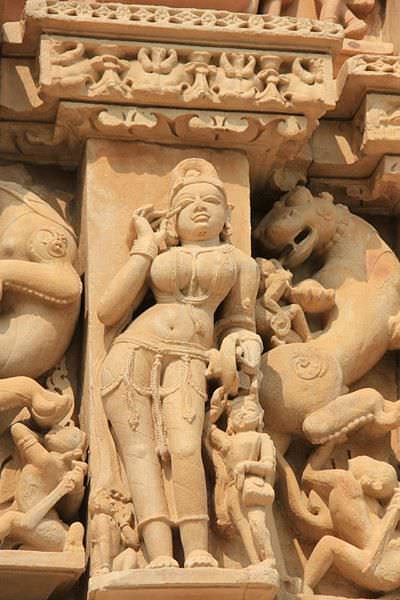
Alasa kanya - a decorative female figure.

Amalaka - a large fluted stone disc placed on top of a Nagara tower taking its form from the amla or myrobalan fruit native to India.
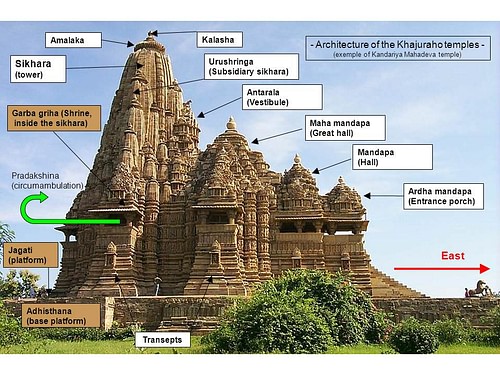
Antarala - an antechamber to the inner sanctum or garbhagriha of a temple.
Ardhamandapa - a temple portico serving as an entrance porch.
Bho - a medallion motif of Orissan architecture which projects from towers and shows a monster regurgitating garlands flanked by two dwarfs.
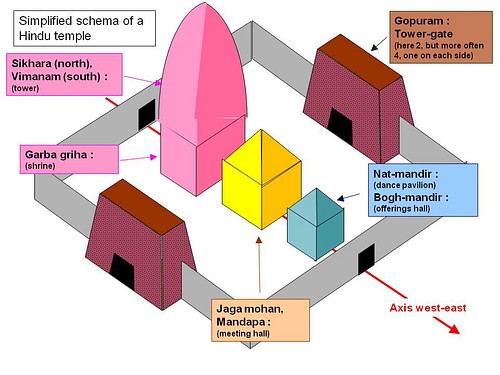
Bhoga mandapa - (or Bogh-mandir) a hall in Orissan temples which is used for consecrated food preparation and distribution.

Devalaya - the general name of a temple meaning a god's dwelling place.
Dravida - the style of southern temple architecture.
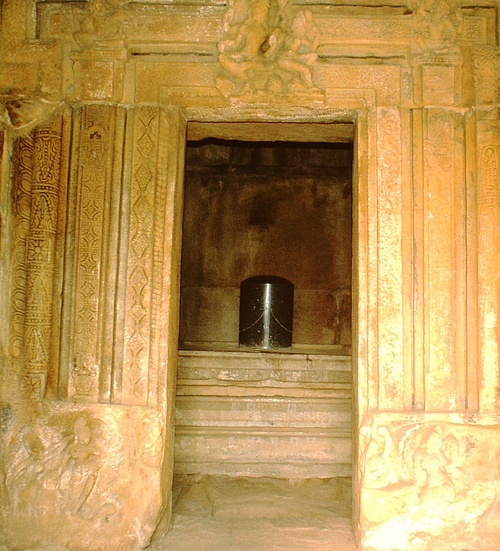
Garbhagriha - (also garbha grha) meaning 'womb-chamber,' the small windowless room that is the main shrine of the temple, usually containing a representation or symbol of the principal deity.
Ghana dvara - blind doorways of the garbhagriha, which symbolically allow the energy of the deity to radiate through and beyond the temple. They may also act as secondary niche shrines.
Ghanta - a bell-shaped finial on the top of a tower.

Gopura - a monumental gate tower of Dravida temples.
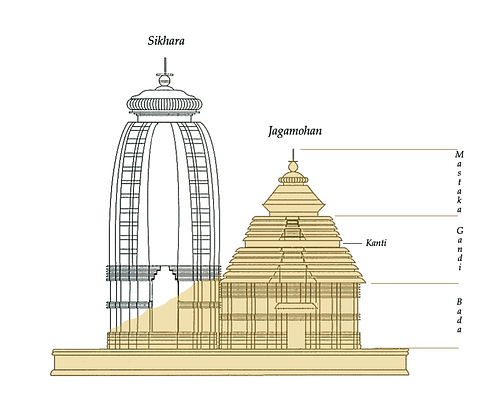
Jagamohana - the mandapa or entrance hall of an Orissan temple.
Kirtimukha - a decorative lion or monster motif with the lower jaw missing, typically placed over doorways.
Mandapa - a columned hallway which leads to the garbhagriha or inner sanctum.
Makara - a decorative sea monster motif.
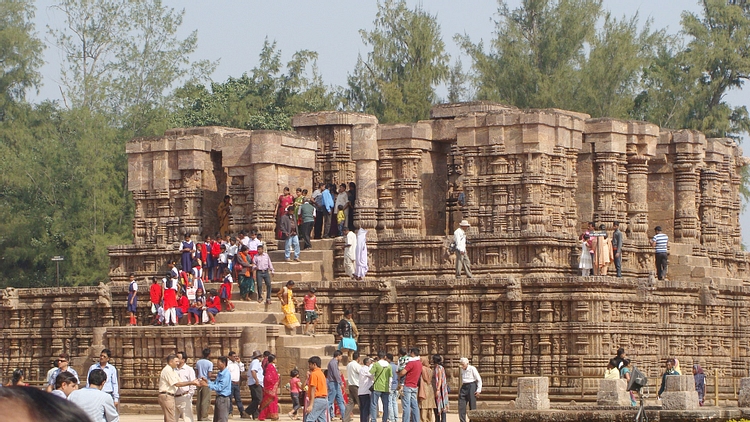
Nagara - the style of northern temple architecture.

Nandi Mandapa - a pavilion which contains a statue of Shiva's gatekeeper and vehicle, the bull Nandi.
Nata mandapa - (also nata mandir) the dance hall in Orissan temples, added from the 10th century CE.
Nataraja - a decorative dancing Shiva motif.

Prakara - a high wall which encloses a temple.
Ratha - a projection on the exterior wall of a Nagara temple; there are typically seven on each side. Also the name for the chariot of the sun god Surya which sun temples represent via spoked wheels on the outer walls.
Sala - a barrel-vaulted roof in Dravida architecture, often represented as an architectural motif.
Sikhara - the tower of a Nagara temple which is built directly above the inner sanctum or garbhagriha. Also the decorative top of a tower in Dravida temples.

Tala - the tiers of a vimana tower.
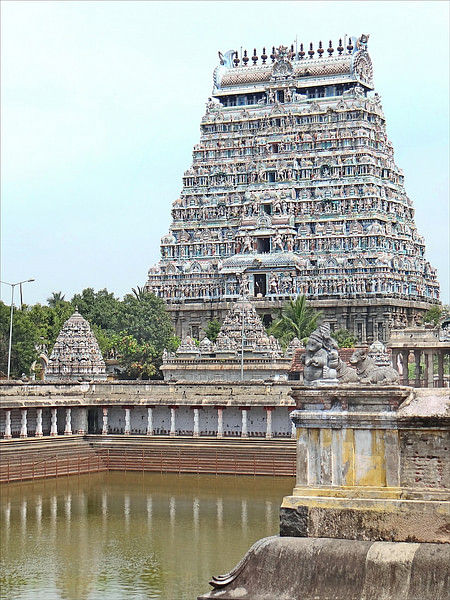

Temple tank - a ritual bathing tank or pool common in southern temples.

Urushringa - a smaller, subsidiary tower, usually joining or enclosing the main tower.

Vimana - the more rounded tower of a Dravida temple. Typically they are topped by a small dome.
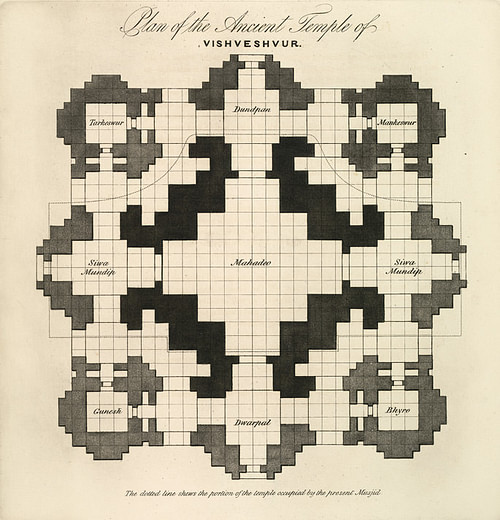
Vastu-purusa-mandala - the symbolic symmetrical floorplan which Hindu temples follow.

Vesara - the style of architecture which mixed Nagara and Dravida styles.
Vyala - (also yali) the decorative lion monster seen in many Hindu temples.