Search
Search Results

Definition
Louis I de Bourbon, Prince of Condé
Louis I de Bourbon (l. 1530-1569) was a descendant of Louis IX of France (r. 1226-1270) and founder of the House of Condé. The Prince of Condé proved his valor as a Huguenot military leader during the first three French Wars of Religion and...

Article
Confucianism in Ancient Korea
Principles of Confucianism were adopted by successive dynasties and kingdoms in ancient Korea, and the study of classic Confucian texts was an important part of education and entrance examinations for the state administration. Confucianism...
Article
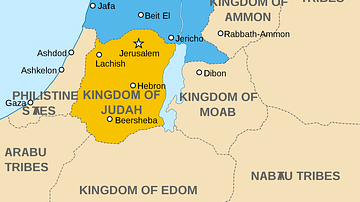
Ancient Israelite & Judean Religion
As early as the 10th century BCE, Israelite and Judean religion began to emerge within the broader West Semitic culture, otherwise known as Canaanite culture. Between the 10th century and 7th centuries BCE, ancient Israelite and Judean religion...

Article
Daily Life in Ancient China
Daily life in ancient China changed through the centuries but reflected the values of the presence of gods and one's ancestors in almost every time period. Villages like Banpo show evidence of a matriarchal society, where there was a priestly...

Article
Daily Life in the Inca Empire
Daily life in the Inca empire was characterised by strong family relationships, agricultural labour, sometimes enforced state or military service for males, and occasional lighter moments of festivities to celebrate important life events...

Article
Inca Mummies
The Inca civilization of Peru, as with many other ancient Andean cultures, mummified many of their dead and buried them with valuable materials such as precious metal jewellery, fine pottery, and sumptuous textiles. Important mummies could...

Definition
Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestant Christians, primarily active in the 16th-18th centuries CE, who claimed the Anglican Church had not distanced itself sufficiently from Catholicism and sought to 'purify' it of Catholic practices. The term...

Definition
Mithra
Mithra is the Persian god of the rising sun, contracts, covenants, and friendship. He also oversaw the orderly change of the seasons, maintained cosmic order, and was responsible for bestowing divine grace on kings, legitimizing their rule...

Definition
Temple
A temple (from the Latin templum) is a structure usually built for the purpose of, and always dedicated to, religious or spiritual activities including prayer, meditation, sacrifice and worship. The templum was a sacred precinct defined by...

Definition
Apis
Apis was the most important and highly regarded bull deity of ancient Egypt. His original name in Egyptian was Api, Hapi, or Hep; Apis is the Greek name. He is not, however, associated with the god Hapi/Hep who was linked to the inundation...