Search
Search Results

Definition
Mesopotamian Government
Ancient Mesopotamian government was based on the understanding that human beings were created to help and serve the gods. The high priest, king, assembly of elders, governors, and any other officials were recognized as stewards chosen by...

Definition
Hammurabi
Hammurabi (r. 1792-1750 BCE) was the sixth king of the Amorite First Dynasty of Babylon best known for his famous law code which served as the model for others, including the Mosaic Law of the Bible. He was the first ruler able to successfully...

Definition
Ishtar
Ishtar (Inanna in Sumerian sources) is a primary Mesopotamian goddess closely associated with love and war. This powerful Mesopotamian goddess is the first known deity for which we have written evidence. While largely unknown in the modern...

Definition
Mesopotamian Religion
Mesopotamian religion was central to the people's lives. Humans were created as co-laborers with their gods to hold off the forces of chaos and to keep the world running smoothly. As in ancient Egypt, the gods were honored daily for providing...

Definition
Astrolabe
The astrolabe is an astronomical instrument used from around the 6th century to measure time and position by determining the altitude of heavenly bodies like the Sun and certain stars. Measurements were taken in reference to the viewer's...

Definition
Tiamat
Tiamat is the Mesopotamian goddess associated with primordial chaos and the salt sea best known from the Babylonian epic Enuma Elish. In all versions of the myth, following the original, Tiamat always symbolizes the forces of chaos, which...

Image
Euclid of Alexandria
An illustration of Euclid of Alexandria, the 4th century BCE mathematician.
Image
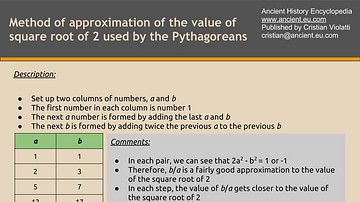
Approximation to the Value of Square Root of 2
This is one of the best methods of approximation to the value of square root of 2 used by the Pythagorean brotherhood.
Image
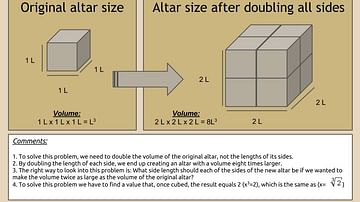
The Delian Problem
The Delian Problem: finding the value of the cube root of 2

Definition
Ancient Greece
Greece is a country in southeastern Europe, known in Greek as Hellas or Ellada, and consisting of a mainland and an archipelago of islands. Ancient Greece is the birthplace of Western philosophy (Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle), literature...