Search
Search Results

Definition
Tympanon
The tympanon (tympanum in Latin) was the most popular frame-drum in ancient Greek music, producing a loud rumbling sound not far from the sound of the orchestral timpani drums today. This percussion instrument was played mainly by women on...

Definition
Idunn
Idunn (pronounced Ih-dune) is a fertility goddess in Norse mythology who holds the apples of eternal youth the gods rely on to remain young and healthy. The Norse gods were not immortal – they just lived very long lives – and the apples of...

Definition
Jeremiah
Jeremiah (c. 650-570 BCE) was a major prophet of Israel in the Hebrew Bible. In addition to his book of prophecy, he is also credited with writing the Books of Kings and Lamentations (perhaps written by his scribe, Baruch). Called to prophecy...

Definition
Tarquinia
Tarquinia (Etruscan name: Tarch'na or Tarch, Roman name: Tarquinii) is a town located on the western coast of central Italy which was an important Etruscan and then Roman settlement. It is famous today as the site of around 200 Etruscan tombs...

Definition
Nicias - The Athenian General
Nicias, or Nikias (c. 470-413 BCE), was a wealthy Athenian politician and general during the Peloponnesian War (431-404 BCE). He became established as a prominent political leader of the aristocratic faction in Athenian politics and generally...

Definition
Hoenir
Hoenir or Hönir (Old Norse: Hœnir or Hønir) is a very shadowy god figure in Norse mythology, who joins the gods Loki and Odin on a couple of occasions in the old texts. He seems to have attributes of creation and prophecy, and his name might...

Definition
Vejovis
Vejovis (sometimes spelt Vediovis) was an obscure Roman deity. He is poorly attested in both written sources and archaeology, and his nature is debated by scholars. His name is related to Jove (Jupiter), and some authors described him as...

Definition
Oribasius
Oribasius (c. 320-400/403 CE) was the physician and political advisor of the Roman emperor Julian the Apostate (r. 361-363 CE). A native of Pergamon, a rich and powerful Greek city in Mysia, he studied medicine and oratory and belonged to...
Definition
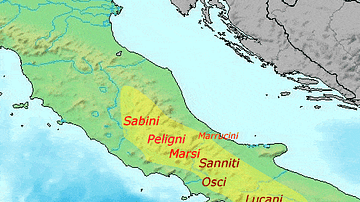
Angitia
Angitia, which also appears epigraphically as Angita, Arigitia or Anguita, was a goddess among the pre-Roman Italic and Oscan-Umbrian peoples of central Italy and believed to have persisted as a domestic cult figure well into the Roman Republic...

Article
Mesopotamian Inventions - Creating the Future
Mesopotamian inventions include many items taken for granted today, most of which were created during the Early Dynastic period (circa 2900-2350/2334 BCE) or developed from achievements of the Uruk period (circa 4000-3100 BCE). The Sumerians...