Search
Did you mean: Heraclius?
Search Results

Definition
Philoctetes
The play Philoctetes was written by one of the greatest of the Greek tragedy playwrights, Sophocles, in 409 BCE. Philoctetes is one of his surviving plays whose exact production date can be determined and is set in the final year of the Trojan...

Article
Elephants in Hellenistic History & Art
Elephants were thought of as fierce and frightful monsters in antiquity, very real though rarely seen until the Hellenistic period. They were deployed on the battlefield to strike terror into the enemy, however, since fear was considered...

Article
Cats in the Ancient World
Cats and humans have shared in each other's lives for thousands of years and, even though they have not always been regarded as highly as in the present, have played an important role in a number of cultures. Always enigmatic, the cat has...

Definition
Hippolyta
Hippolyta, or Hippolyte, was a queen of the Amazons in Greek mythology. A daughter of Ares, the Greek god of war, and Otrera, queen of the Amazons, she is a significant figure in the legends of Hercules and Theseus. In the present day, she...

Definition
Ninurta
Ninurta (identified with Ningirsu, Pabilsag, and the biblical Nimrod) is the Sumerian and Akkadian hero-god of war, hunting, and the south wind. He first appears in texts in the early 3rd millennium BCE as an agricultural god and local deity...

Article
Herodotus on Animal Sacrifice in Egypt
II:38. The males of the ox kind they consider to belong to Epaphos, and on account of him they test them in the following manner: If the priest sees one single black hair upon the beast he counts it not clean for sacrifice; and one of the...

Definition
Crates of Thebes
Crates of Thebes (l. c. 360-280 BCE) was one of the most important Cynic philosophers of ancient Greece. He was born to a wealthy family in Thebes but gave away his inheritance after realizing the futility of material possessions. He then...

Definition
Hercules
Hercules (Herakles) was a hero of Greek mythology famous for his great strength and endurance. Celebrated as an extraordinary mortal, his success in seemingly impossible labours won him an immortal place amongst the gods. As the greatest...

Article
Alexander the Great as a God
The age-old concept of the “divine right of kings” allowed that a country's ruler received his or her power or authority from God. However, few, if any, were delusional enough to actually believe themselves to be a god. An exception to this...
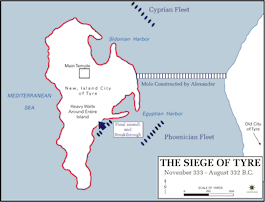
Article
Alexander's Siege of Tyre, 332 BCE
After defeating Darius III at the battle of Issus in November 333 BCE, Alexander marched his army (about 35,000-40,000 strong) into Phoenicia, where he received the capitulation of Byblus and Sidon. Tyrian envoys met with Alexander whilst...