Search
Search Results

Article
The Salt Trade of Ancient West Africa
Salt from the Sahara desert was one of the major trade goods of ancient West Africa where very little naturally occurring deposits of the mineral could be found. Transported via camel caravans and by boat along such rivers as the Niger and...

Article
The Railways in the British Industrial Revolution
The railways were perhaps the most visible element of the Industrial Revolution for many. Trains powered by steam engines carried goods and people faster than ever before and reached new destinations, connecting businesses to new markets...
Article
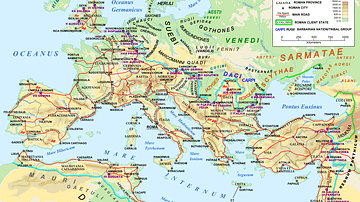
Slavery in the Roman World
Slavery was an ever-present feature of the Roman world. Slaves served in households, agriculture, mines, the military, workshops, construction and many services. As many as 1 in 3 of the population in Italy or 1 in 5 across the empire were...

Article
Slavery in Plantation Agriculture
The first plantations in the Americas of sugar cane, cocoa, tobacco, and cotton were maintained and harvested by African slaves controlled by European masters. When African slavery was largely abolished in the mid-1800s, the center of plantation...

Article
Laocoön: The Suffering of a Trojan Priest & Its Afterlife
The sculpture group of Laocoön and His Sons, on display in the Vatican since its rediscovery in 1506, depicts the suffering of the Trojan prince and priest Laocoön (brother of Anchises) and his young sons Antiphantes and Thymbraeus and is...

Article
Sydney Harbour Bridge Construction
The Sydney Harbour Bridge – affectionately known as The Coathanger by Australians – was opened to great fanfare and a touch of scandal on 19 March 1932 and was the longest steel arch bridge in the world at the time, with a span of 503 metres...

Article
Ancient History Encyclopedia in Japan
The “Ancient Japan” initiative at Ancient History Encyclopedia arose as there is a dearth of open access and digitally curated information concerning early Japanese history available online and in English. East and Southeast Asia are arguably...

Article
Top 5 'Deep-Dive' Virtual Shipwrecks
According to UNESCO, an estimated three million shipwrecks are scattered in the oceans’ deep canyons, trenches, and coral reefs and remain undiscovered. These shipwrecks preserve historical information and provide clues about how people lived...

Definition
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire (1206-1368) was founded by Genghis Khan (r. 1206-1227), first Great Khan or 'universal ruler' of the Mongol peoples. Genghis forged the empire by uniting nomadic tribes of the Asian steppe and creating a devastatingly effective...

Definition
Roman Architecture
Roman architecture continued the legacy left by Greek architects and the established architectural orders, especially the Corinthian. The Romans were also innovators and they combined new construction techniques and materials with creative...