Search
Search Results

Definition
Demetrius I of Macedon
Demetrius I of Macedon, also known as Demetrios Poliorcetes, the 'Besieger' (c. 336 - c. 282 BCE), was a Macedonian king who, along with his father Antigonus I, fought for control of Alexander the Great's empire in the 'Successor Wars'. After...

Article
Elephants in Hellenistic History & Art
Elephants were thought of as fierce and frightful monsters in antiquity, very real though rarely seen until the Hellenistic period. They were deployed on the battlefield to strike terror into the enemy, however, since fear was considered...

Article
The Hellenistic World: The World of Alexander the Great
The Hellenistic World (from the Greek word Hellas for Greece) is the known world after the conquests of Alexander the Great and corresponds roughly with the Hellenistic Period of ancient Greece, from 323 BCE (Alexander's death) to the annexation...

Definition
Cyrene
Cyrene (modern-day Shahhat, Libya) was a vital cultural center and port of trade in North Africa founded in 631 BCE by Greek colonists from the island of Thera. The city is best known as the birthplace of the philosopher Aristippus of Cyrene...

Article
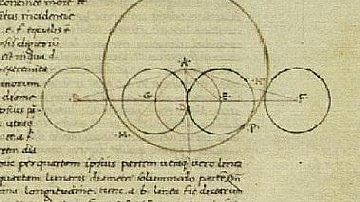
Greek Mathematics
Greek mathematics, the study of numbers and their properties, patterns, structure, space, apparent change, and measurement, is said to have originated with Thales of Miletus (l. c. 585 BCE) but was clearly understood during the periods of...
Definition
Greek Astronomy
Ancient Greek astronomy was the study of the universe to understand how it functioned and why apart from the established theistic model that claimed all things were ordered and maintained by the gods. Ancient Greek astronomers relied on observation...

Definition
Rosetta Stone
The Rosetta Stone is an incomplete grey and pink granodiorite stela dating from 196 BCE which presents a priestly decree concerning King Ptolemy V of Egypt. The text is in three different versions: Hieroglyphic, Demotic and Greek, a fact...

Definition
Hipparchus of Nicea
Hipparchus of Nicea (l. c. 190 - c. 120 BCE) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician regarded as the greatest astronomer of antiquity and one of the greatest of all time. He is best known for his discovery of the precession...

Definition
Library of Pergamon
The Library of Pergamon was established in the city of Pergamon (also Pergamum) by the Attalid King Eumenes II (r. 197-159 BCE) and became the most famous and well-respected center of learning after the Library at Alexandria, Egypt. The library...

Definition
Ptolemaic Army
The army of Ptolemaic Egypt was a well-organized fighting force trained in Hellenistic warfare. The Ptolemaic dynasty used their considerable wealth to maintain a large standing army of professional soldiers. Some troops were paid in money...