Illustration
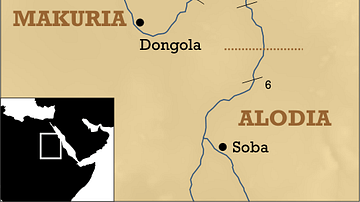
The Temple of Dakka is a Meroitic, Ptolemaic and Roman temple located in New Wadi es-Sebua, a temple complex area in southern Egypt located on the banks of Lake Nasser. It was placed in its present location as part of the large rescue effort led by UNESCO to save the ancient monuments of Lower Nubia from the waters of Lake Nasser. The temple was first begun in the 3rd century BCE by Kushite King of Meroe Arkamani (or Ergamenes II) in collaboration with Ptolemy IV (r. 221 – 204 BCE), who dedicated it to the god Thoth. Its construction continued in the reigns of later Ptolemies, and Roman emperors Augustus (r. 27 BCE - 14 CE) and Tiberius (r. 14 to 37 CE) who enlarged the structure by constructing a massive 12-metre-high pylon.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Raddato, C. (2022, March 13). Temple of Dakka, Egypt. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/15407/temple-of-dakka-egypt/
Chicago Style
Raddato, Carole. "Temple of Dakka, Egypt." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified March 13, 2022. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/15407/temple-of-dakka-egypt/.
MLA Style
Raddato, Carole. "Temple of Dakka, Egypt." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 13 Mar 2022. Web. 29 Mar 2025.