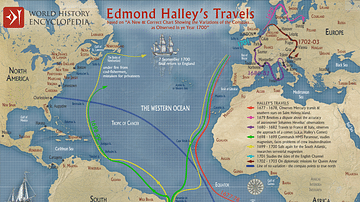
Illustration
The Scientific Revolution in Europe, roughly 1500 to 1700, was a profound intellectual and cultural transformation that forever altered humanity's understanding of the natural world. The period witnessed a seismic shift from medieval beliefs and superstitions to an empirical and evidence-based approach to science and exploration and saw significant breakthroughs and developments in maths, physics, chemistry, and biology and the emergence of modern science.
Prominent figures like Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, Francis Bacon, and Isaac Newton challenged the geocentric model of the universe, developed the laws of motion and gravitation, and laid the groundwork for modern physics and astronomy. The Scientific Revolution paved the way for the scientific method, critical thinking, and the notion that scientific developments would improve our understanding of the natural world.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2023, October 12). The Scientific Revolution in Europe. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/18023/the-scientific-revolution-in-europe/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Scientific Revolution in Europe." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified October 12, 2023. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/18023/the-scientific-revolution-in-europe/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Scientific Revolution in Europe." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 12 Oct 2023. Web. 16 Apr 2025.