Illustration
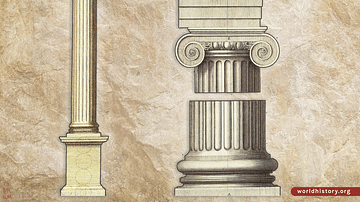
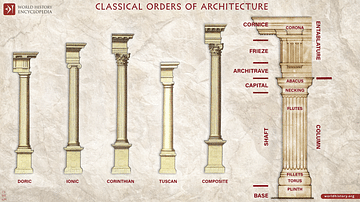
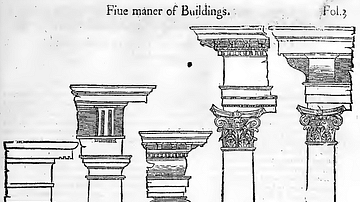
The Classical Orders of Architecture (Doric, Ionic, Corinthian, Tuscan, and Composite), originating in ancient Greece and refined by the Romans, are fundamental design principles that significantly influence classical and neoclassical structures. The Doric Order, characterized by its straightforward and robust design, reflects the simplicity and strength valued in ancient Greek architecture. Developed during the 7th century BCE, the Doric Order features sturdy columns with fluted shafts and unadorned capitals. It represents a timeless expression of architectural integrity and has been embraced in various historical and contemporary constructions.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2023, December 12). The Doric Order, Classical Orders of Architecture. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/18240/the-doric-order-classical-orders-of-architecture/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Doric Order, Classical Orders of Architecture." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified December 12, 2023. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/18240/the-doric-order-classical-orders-of-architecture/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Doric Order, Classical Orders of Architecture." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 12 Dec 2023. Web. 14 Apr 2025.