Search
Remove Ads
Advertisement
Summary 
Loading AI-generated summary based on World History Encyclopedia articles ...
Search Results

Definition
Amorite
The Amorites were a Semitic people who seem to have emerged from western Mesopotamia (modern-day Syria) at some point prior to the 3rd millennium BCE. In Sumerian they were known as the Martu or the Tidnum (in the Ur III Period), in Akkadian...

Image
Amorite pottery juglet
Amorite, about 2400-2000 BC From the Middle Euphrates region, Syria This juglet, with its applied figurine, is pierced at the base and may have been a strainer. Alternatively it could have been used a sprinkler, by clamping a thumb over...
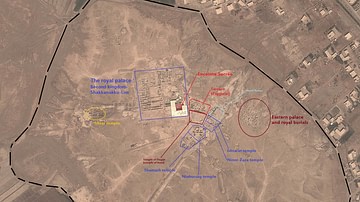
Definition
Mari
Mari was a city-state located near the west bank of the Euphrates River in Northern Mesopotamia (now eastern Syria) during the Early Bronze Age and the Middle Bronze Age. One of the earliest known planned cities, Mari is believed to have...

Definition
Hammurabi
Hammurabi (r. 1792-1750 BCE) was the sixth king of the Amorite First Dynasty of Babylon best known for his famous law code which served as the model for others, including the Mosaic Law of the Bible. He was the first ruler able to successfully...

Image
A portion of wall at Mari
A portion of the fortifications at the site of Mari, modern-day Tell Hariri, Syria. Mari's fortifications entered their most advanced stage in the 19th century BCE when the city and the rest of the region were under threat from Amorite invaders...

Definition
Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi was a set of 282 laws inscribed in stone by the Babylonian king Hammurabi (r. 1795-1750 BCE) who conquered and then ruled ancient Mesopotamia. Although his law code was not the first, it was the most clearly defined...

Video
The History of Egypt: The Hyksos (Part 3)
The Hyksos are mentioned in the Bible but are referred to as "Amorites". The Amorite Empire flourished across the entire middle east from 1800 B.C.E. until 1550 B.C.E. Dr. Neiman explains the difference between the Amorite empire of the...

Definition
Sumerians
The Sumerians were the people of southern Mesopotamia whose civilization flourished between c. 4100-1750 BCE. Their name comes from the region which is frequently – and incorrectly – referred to as a “country”. Sumer was never a cohesive...
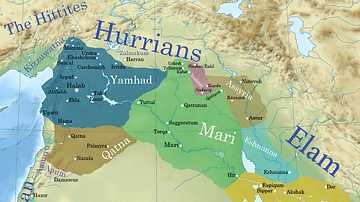
Image
Ancient Syro-Mesopotamia ca. 1764 BCE
This map shows the political situation in Syro-Mesopotamia c. 1764 BCE. During this time, the Amorite Kings, Hammurabi of Babylon and Zimri-Lim of Mari were engaged in near-constant warfare with surrounding polities, many of whom were also...

Definition
Ur
Ur was a city in the region of Sumer, southern Mesopotamia, and its ruins lie in what is modern-day Tell el-Muqayyar, Iraq. According to biblical tradition, the city is named after the man who founded the first settlement there, Ur, though...