Search
Remove Ads
Advertisement
Summary 
Loading AI-generated summary based on World History Encyclopedia articles ...
Search Results

Definition
Confucius
Confucius (Kongzi) was a 6th century BCE Chinese philosopher. His thoughts, expressed in the philosophy of Confucianism, have influenced Chinese culture right up to the present day. Confucius is a larger than life figure and it is difficult...

Image
Confucius
A statue of Confucius, located in Hunan, China on the shore of the Dongting Lake. No contemporary physical likeness exists of the Chinese philosopher Confucius (c. 551 to c. 479 BCE) but he is most often represented as an old man with long...

Definition
Confucianism
Confucianism is a philosophy developed in 6th-century BCE China, which is considered by some a secular-humanist belief system, by some a religion, and by others a social code. The broad range of subjects touched on by Confucianism lends itself...
Definition
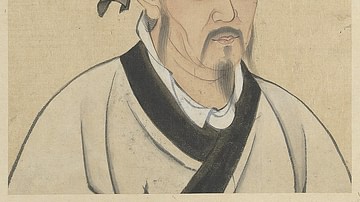
Mencius
Mencius (l. 372-289 BCE, also known as Mang-Tze or Mang-Tzu) was a Confucian philosopher during The Warring States Period in China (c. 481-221 BCE) and is considered the greatest after Confucius himself for his interpretation, formulation...

Definition
Qilin (Chinese Unicorn)
The qilin (麒麟, or simply lin 麟) is a Chinese mythical creature, frequently translated as "Chinese unicorn." While this term may suggest a one-horned creature, the qilin is often depicted with two horns. However, like the Western unicorn...

Image
Confucius by Wu Daozi
No contemporary portrait of the Chinese philosopher Confucius (c. 551 to c. 479 BCE) survives but the most popular print during the Imperial period was taken from a now lost original by Wu Daozi (Wu Taoutsi) in the 8th century CE.

Image
Confucius, Buddha and Lao-Tzu
A Qing Dynasty print showing Confucius presenting Gautama Buddha to the philosopher Lao-Tzu.
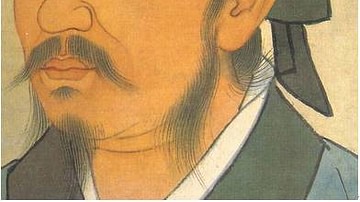
Definition
Xunzi
Xunzi (pronounced shund-zee, l. c. 310-c. 235 BCE) was a Confucian philosopher of the Warring States Period (c. 481-221 BCE) in China. He is also known as Hun Kuang, Hsun Tzu, Xun Tzu, and Xun Kuang. Xunxi translates as Master Xun and is...

Image
Commentaries of the Analects of Confucius
A copy of Zhu Xi's commentary on the 'Analects' of Confucius, printed during the Ming dynasty.

Definition
Lao-Tzu
Lao-Tzu (l. c. 500 BCE, also known as Laozi or Lao-Tze) was a Chinese philosopher credited with founding the philosophical system of Taoism. He is best known as the author of the Laozi (later retitled the Tao-Te-Ching translated as “The Way...