Search
Remove Ads
Advertisement
Summary 
Loading AI-generated summary based on World History Encyclopedia articles ...
Search Results

Definition
Wu Zetian
Empress Wu Zetian (Empress Consort Wu, Wu Hou, Wu Mei Niang, Mei-Niang, and Wu Zhao, l. 624-705 CE, r. 690-704 CE) was the only female emperor of Imperial China. She reigned during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) and was one of the most effective...

Definition
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang
Xuanzong (birth name, Li Longji, l. 685-762 CE, r. 712-756 CE) was the 7th emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China, whose domestic and foreign policies established the Tang Dynasty as the Golden Age in Chinese history. Many of the most important...

Definition
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) was one of the greatest in Imperial Chinese history. It was a golden age of reform and cultural advancement which lay the foundation for policies which are still observed in China today. The second emperor, Taizong...

Image
Wu Zetian's Stele
Wu Zetian's (r. 683-704 CE) Stele at Quianling Mausoleum where she was buried along with her husband Gaozong.

Video
Wu Zetian: the First and Only Empress of Imperial China
Wu Zetian was born in 624 CE to a wealthy family, and her father encouraged her to learn how to read and write, as well as how to play music, the art of public speaking, and how to compose poetry, even though these skills were usually reserved...

Image
Empress Wu Zetian
Empress Wu Zetian (r. 683-704 CE) of the Tang Dynasty. Image taken from An 18th-century album of portraits of 86 emperors of China, with Chinese historical notes. Originally published/produced in China, 18th century. (British Library, Shelfmark...
Image
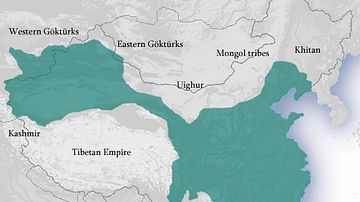
China during Wu Zetian's Reign
Map of China showing the Wu Zetian's empire c. 700 CE.

Definition
Emperor Taizong of Tang
Taizong (birth name, Li-Shimin, l. 598-649 CE, r. 626-649 CE) was the second emperor of the Tang Dynasty and is considered one of the greatest rulers in Chinese history for his reforms of the government and the laws, his religious tolerance...

Definition
Ancient China
Ancient China produced what has become the oldest extant culture in the world. The name 'China' comes from the Sanskrit Cina (derived from the name of the Chinese Qin Dynasty, pronounced 'Chin') which was translated as 'Cin' by the Persians...

Article
Women in Ancient China
Women in ancient China did not enjoy the status, either social or political, afforded to men. Women were subordinate to first their fathers, then their husbands, and finally, in the case of being left a widow, their sons in a system known...