Search Definitions
Browse Content (p. 24)

Definition
George Berkeley
George Berkeley (1685-1753) was an Anglo-Irish bishop and an empiricist and idealist philosopher. He infamously claimed that no matter exists outside of God and that things only exist outside of our minds and perceptions because God perceives...

Definition
Ivan III of Russia
Ivan III of Russia (Ivan the Great) was the Grand Prince of Moscow and Russia from 1462 to 1505. Ivan III was born in 1440 to Grand Prince Vasily II of Moscow (r. 1425-1462) and his wife, Maria Borovsk (l. c. 1420-1485). He served as co-ruler...

Definition
Baruch Spinoza
Baruch Spinoza (1632-1677) was a Dutch philosopher who combined rationalism and metaphysics to create a unique system of thought. Spinoza was held up as an atheist philosopher in the 18th century, but this is not an entirely accurate representation...
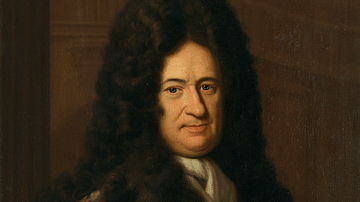
Definition
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646-1716) was a German polymath who became well-known across Europe for his work, particularly in the fields of science, mathematics, and philosophy. Leibniz's rationalist philosophy attempted to reconcile traditional...

Definition
Kremlin
The Kremlin is a fortified complex located in the centre of Moscow, Russia, which is made up of towers, high walls, palaces, and cathedrals. Construction of the Kremlin began as early as the 12th century. As one of Russia's most famous landmarks...

Definition
Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) was a French scientist, mathematician, and philosopher whose work influenced both the Scientific Revolution and later European thought. Pascal is known for his practical achievements in science, such as a calculating...

Definition
Patrick Henry
Patrick Henry (1736-1799) was a Virginian lawyer and politician who played a vital role in the American Revolution (c. 1765-1789). Known for his brilliant oration, including the famous Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death speech, Henry served...

Definition
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) was a German Enlightenment thinker who is widely regarded as one of the most important philosophers of any period. His most famous works of critical philosophy include The Critique of Pure Reason, which challenged...

Definition
Medes
The Medes or Medians were a group of Indo-Iranian-speaking people from central Asia who migrated westwards and entered northern Iran around the end of the 2nd millennium BCE. They settled in the highlands of Zagros (Zagreus in Greek) and...

Definition
Cheyenne
The Cheyenne are a North American Native nation, originally from the Great Lakes region, who migrated to modern-day Minnesota and then to areas in North Dakota and further southwest. They are associated with the Plains Indians culture and...