Search Definitions
Browse Content (p. 70)

Definition
Jeremiah
Jeremiah (c. 650-570 BCE) was a major prophet of Israel in the Hebrew Bible. In addition to his book of prophecy, he is also credited with writing the Books of Kings and Lamentations (perhaps written by his scribe, Baruch). Called to prophecy...

Definition
Archimedes
Archimedes (l. 287-212 BCE) was a Greek engineer and inventor who is regarded as the greatest mathematician of antiquity and one the greatest of all time. He is credited with a number of inventions still in use today (such as the Archimedes...

Definition
Ezekiel
Ezekiel was both a priest and a prophet who lived in the 6th century BCE. The prophets of Israel were oracles (a term for a person as well as a place) for ways in which humans communicated with their gods. The oracle was possessed by the...

Definition
Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne (1839-1906) was a French post-impressionist artist. Although he struggled for recognition in his own lifetime and often lacked confidence in his work, the artist's unique style, use of light and colour, and his interest in geometric...

Definition
Samson
Samson was one of the last judges in the Hebrew Book of Judges who arose as a leader of the Jews when they settled in Canaan. He was a Nazirite, known for his incredible strength, the secret of which was discovered by Delilah who betrayed...

Definition
Plebeians
Plebeians were members of the plebs, the hereditary social class of commoners in ancient Rome. Their exclusion from political power by the patricians, who claimed to be the descendants of the first senators, led to Conflict of the Orders...

Definition
Pyrrho
Pyrrho of Elis (l. c. 360 to c. 270 BCE) was a Greek skeptic philosopher credited with founding the school of Pyrrhonism which taught that one must resist making judgments or stating conclusions because sense perception did not correlate...

Definition
Book of Job
The book of Job in the Hebrew Bible is found among the books designated Ketuvim ("writings"), along with Ecclesiastes and the Book of Proverbs. All three belong to a genre known as wisdom literature. The books share a common ancient cultural...

Definition
Nicodemus
Nicodemus was an early follower of Jesus Christ, uniquely mentioned only in the fourth gospel, the Gospel of John. According to that gospel, he was a Pharisee and a member of the Sanhedrin (the Jewish Council) in Jerusalem at the time of...
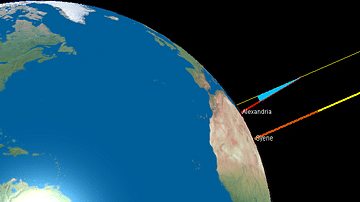
Definition
Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes (l. c. 276-195 BCE) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, mathematician, and poet best known for being the first to calculate the circumference of the earth and its axial tilt. He is also recognized for his mathematical innovation...