Search Images
Browse Content (p. 1690)

Image
Stamped Mud Brick, Babylonia, Mesopotamia
This is a stamped mud brick with cuneiform inscriptions, which lies within a building's wall in ancient Babylonia (modern Babylon governorate), Mesopotamia, Iraq.

Image
Stela of Iddi-Sin, King of Simurrum
The stela of Iddi-Sin, King of Simurrum celebrates and commemorates the victories of this King against his enemies, mostly tribes of West Iran. The stela is carved with 108 lines of cuneiform inscriptions and was found at Qarachatan, Pira...

Image
South Side, Ara Pacis
The Ara Pacis Augustae or Altar of the Augustan Peace in Rome (south entrance). Built to celebrate the return of Augustus to Rome in 13 BCE following campaigns in Spain and Gaul, it is a masterpiece of Roman sculpture and, in particular...

Image
Procession Relief, Ara Pacis
A portion of the marble procession relief from the Ara Pacis Augustae in Rome, c. 9 BCE. The hooded figure has been identified as Agrippa. (Museo dell'Ara Pacis, Rome)

Image
Ara Pacis Augustae
The Ara Pacis Augustae or Altar of the Augustan Peace in Rome. Built to celebrate the return of Augustus to Rome in 13 BCE following campaigns in Spain and Gaul, it is a masterpiece of Roman sculpture and, in particular, portraiture. Officials...
Image
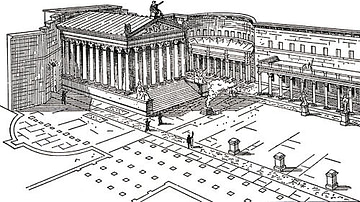
Forum of Augustus, Rome
A reconstruction of the Forum of Augustus in Rome with the temple of Mars Ultor, late 1st century BCE.

Image
Headdress of Motecuhzoma II
The headdress of Motecuhzoma II, Aztec ruler 1502-1520 CE. Although there is no evidence that it was ever worn by Motecuhzoma the headdress may have been amongst the gifts he gave to Cortés, who in turn passed them on to Charles V. This is...

Image
Egg and Dart Ornamentation
The egg and dart ornamentation is a common feature of Classical architecture, used especially to decorate a cornice. This example comes from the 5th century BCE Temple of Apollo on Delos.

Image
Old Silenus
A statue of a comic actor in the costume of Old Silenus, a companion and teacher of Dionysos, the god of wine. He holds a drum and has an empty wine skin over his shoulder. 2nd-1st century BCE, Delos. (Site Museum, Delos)
Image
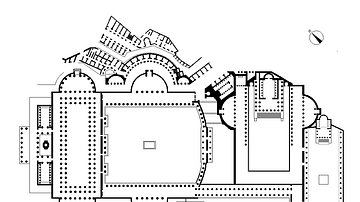
Imperial Fora, Rome
A diagram of the Imperial Fora of Rome. In the centre is Trajan's Forum and above it the semicircular-fronted Trajan's Market. On the left is the Basilica Ulpia. To the right is the Forum of Augustus and below it Caesar's Forum. On the far...